Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) uses heat to destroy tissue. For pain management, radio waves are sent through a precisely placed needle to heat an area of the nerve. This prevents pain signals from being sent back to your brain. RFA is considered for long-term pain conditions, especially of the neck, lower back or arthritic joints that haven’t been successfully treated with other methods.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
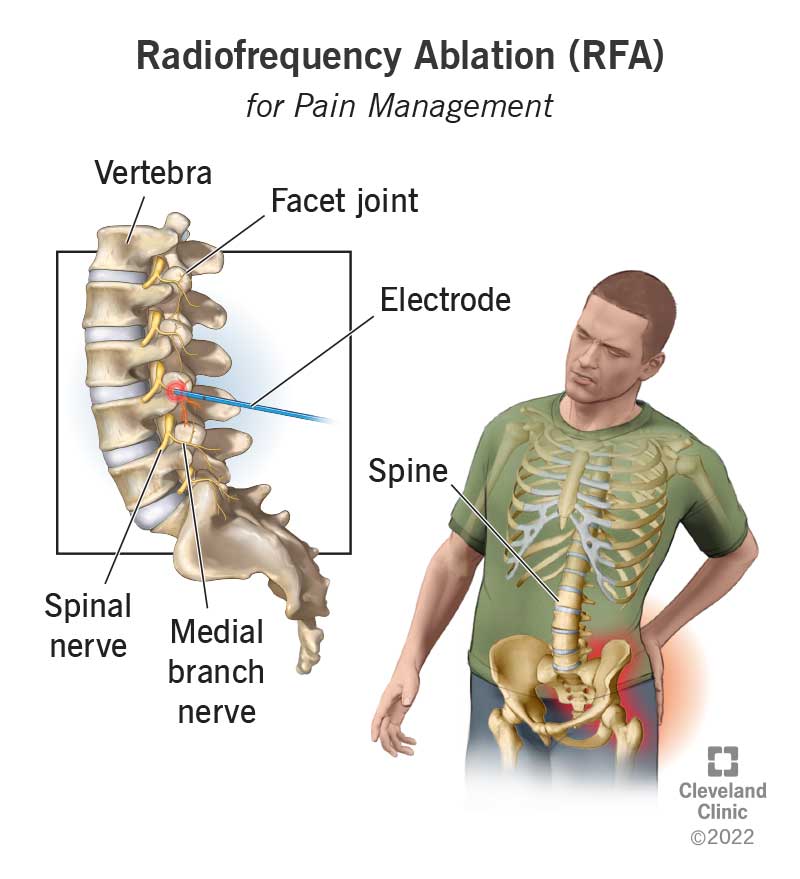
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/17411-radiofrequency-ablation-illustration)
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA), also called radiofrequency neurotomy, uses radio waves to create a current that heats a small area of nerve tissue. The heat destroys that area of the nerve, stopping it from sending pain signals to your brain. RFA can provide lasting relief for people with chronic pain, especially in the lower back, neck and arthritic joints.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
The goals of radiofrequency ablation are to:
Radiofrequency ablation is used to treat:
Radiofrequency ablation uses heat produced from radio waves to target diseased tissue. When radiofrequency is applied to nerve tissue, it damages nerves, which prevents or stops the pain signal from reaching the brain and results in pain relief.
During a radiofrequency ablation procedure, a small hollow needle is inserted into the targeted nerve that is causing pain. An electrode is inserted into the top of the needle, which sends the radio waves through the needle to the targeted nerve. The heat causes a lesion that prevents the nerve from sending pain signals to your brain. Nearby healthy nerves are not damaged during the procedure.
Radiofrequency ablation is often used to manage pain originating from joints (such as your knee) and oftentimes related to pain from your spine, especially your neck and lower back (lumbar area of your spine).
Advertisement
Within your spine, nerves branch off from your spinal cord and travel to the facet joints and sacroiliac joints.
Facet joints are pairs of small joints between the vertebrae in your spine. These joints give your spine flexibility and allow movement of your back, such as twisting and bending. Two small nerves, called medial branch nerves, are connected to the facet joints and send a signal to your brain that there is pain coming from these joints.
Sacroiliac joints are found near the bottom of your spine, right above your tailbone. Lateral branch nerves that are connected to these joints send pain signals from the spine to your brain.
Using radiofrequency ablation to treat the targeted medial branch nerve in the facet joints or the lateral branch nerve in the sacroiliac joints decreases pain signals from reaching your brain.
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) may be right for you if have:
You may not be a candidate for radiofrequency ablation if you:
Your healthcare provider will review your medical and medication history and ask you questions about your pain. If you take aspirin or other blood-thinning medications, you may need to stop taking them for a few days before the procedure.
Your provider will examine you and order X-rays or other imaging tests that are typically ordered to see your anatomy, determine the level of arthritis or other spine injury and rule out any other causes.
Your provider will perform a test, called a diagnostic block, to confirm the source and level of your pain, which can then predict the potential level of your pain relief. The block consists of an injection of a local anesthetic near the area of pain. If the diagnostic block doesn’t provide significant relief, you may not benefit from RFA. If you have a favorable response to the diagnostic block, your provider may recommend RFA as a treatment to ease your pain.
First, you’ll lie on your stomach on a special X-ray table. Your healthcare provider will use monitors to watch your condition during the procedure. You’ll remain aware so you can answer your provider’s questions during the procedure. Medications can be given during the procedure to relax you but this is optional.
Advertisement
Your doctor will use a local anesthetic to numb the area of your skin where a needle will be inserted. Then:
Radiofrequency ablation takes from 15 minutes to two hours to complete, depending on the treatment location and number of treatments performed.
After your radiofrequency ablation procedure:
Advertisement
Your provider may have also recommended physical therapy to regain strength and flexibility. You’ll also have a follow-up appointment to check on your progress and to have any questions you may have answered.
Advantages of radiofrequency ablation include:
During the procedure, you may experience some pain or burning sensation at the site, similar to what you experienced before the procedure. The pain may last for a week or two after the procedure. Applying an ice pack at the site, 20 minutes off and on, may help relieve the pain.
You may feel some temporary numbness where the needle entered your skin.
The risk of complications from RFA is very low. On occasion, permanent nerve damage or pain can occur. In some people, their original pain may get worse. Other complications, including infection and bleeding at the needle insertion site, are uncommon.
Most people have some pain relief after radiofrequency ablation, but the amount varies by cause of pain and location. Pain relief can be immediate in some people, occur within 10 days in other people or may take up to three weeks in others.
Advertisement
Pain relief can last from six months to 12 months. For some people, the relief lasts a few years. Others may have only limited pain relief.
The treated nerve can regrow. If this happens, it usually happens about six to 12 months after the procedure. Radiofrequency ablation can be repeated if needed.
Talk with your healthcare provider about the success rate of your procedure and the length your pain relief may last. Your provider will give you their best projection based on the specific cause, location and severity of your pain.
Call your healthcare provider if you:
Radiofrequency ablation is not considered a surgery. It’s considered a minimally invasive procedure. This means the procedure is performed using methods that access your body with the least amount of damage or disruption to your skin and tissues. In general, minimally invasive treatment methods lower the risk of infection and other complications, reduce the length of hospital stay, lessen the amount of pain experienced and shorten recovery time.
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) uses heat to destroy tissue. When used for pain management, heat is used to target specific nerves that cause you pain. Heating the nerve stops or reduces pain signals from reaching your brain. RFA is considered for long-time pain conditions involving your spine after other methods, such as pain medication and physical therapy have not been successful. RFA is helpful for many people who decide to have the procedure. Talk with your provider to see if RFA is right for you.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Comprehensive pain recovery treatment plans can help you manage your pain levels and symptoms more easily.
