Erythropoietin is a hormone that your kidneys naturally make to stimulate the production of red blood cells. Health problems can occur if your erythropoietin levels are too high or low. Healthcare providers measure your erythropoietin levels with a blood test.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
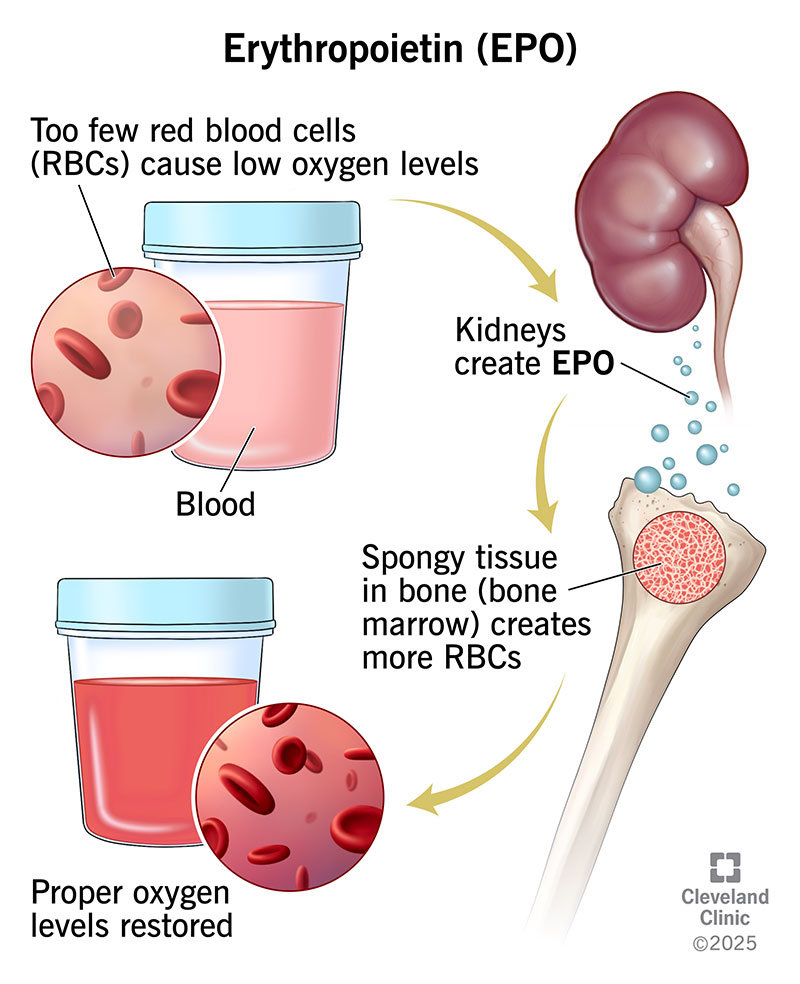
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/erythropoietin)
Erythropoietin is a hormone that your kidneys mainly produce. Erythropoietin (ih-rith-roh-POY-uh-tin) helps your body maintain a healthy amount of red blood cells (erythrocytes).
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
There’s also a synthetic (human-made) form of erythropoietin. Healthcare providers use it to treat anemia that results from chronic kidney disease (CKD). Some athletes improperly use synthetic erythropoietin to help boost performance. It increases the amount of oxygen in your muscles. More oxygen in your muscles gives you more energy. Synthetic EPO is banned in many professional sports and athletic competitions.
Other names for erythropoietin include:
Erythropoietin helps make red blood cells. Red blood cells deliver oxygen to the tissues in your body. Oxygen turns into energy, and your tissues release carbon dioxide. Your red blood cells also transport carbon dioxide to your lungs for you to breathe out.
Normally, when specialized cells in your kidneys detect low blood oxygen levels, they increase the production of EPO. EPO then tells the spongy tissue in your bones (bone marrow) to make more red blood cells.
When cells in your kidneys sense there’s enough oxygen in your blood, they tell your kidneys to make less EPO.
Certain conditions can affect how much EPO your kidneys make. They may cause your kidneys to make too much or not enough. This may cause low or high levels of red blood cells.
Advertisement
A healthcare provider can measure your EPO levels with a blood test. Blood tests help your provider figure out what’s affecting how your body releases EPO. Your provider will take a sample of your blood and send it to a lab for analysis. Once the lab finishes its testing, your provider will contact you to discuss your test results and answer any questions.
Healthcare providers measure erythropoietin in your blood in milliunits per milliliter (mU/mL). A normal range may be between 4 and 26 mU/mL.
Your EPO test results may vary according to several factors. These may include your:
Your provider will carefully interpret your results. They’ll let you know if they’re in or out of range. Even if your EPO levels are within a normal range, you may still need treatment.
Inappropriately high levels of erythropoietin can cause high levels of red blood cells. Another name for high red blood cell levels is polycythemia. Polycythemia causes your blood to thicken.
High levels of EPO may result from:
Chronic kidney disease is the most common cause of low EPO levels. Damaged kidneys can’t make as much EPO. CKD and low EPO levels can lead to anemia.
Polycythemia vera (PV) can also lead to low EPO levels. PV is a type of blood cancer. A genetic mutation causes your bone marrow to make too many red blood cells. It causes low EPO levels because your kidneys sense that you have enough red blood cells. As a result, they don’t make as much EPO.
Treating low levels of EPO requires treating the underlying cause.
The most common treatment is recombinant erythropoietin (erythropoietin-stimulating agents or ESAs). This is a synthetic version of natural EPO. Healthcare providers clone the gene for EPO to cause your body to make more red blood cells. They give it to you as a shot (epoetin alfa injection).
Providers use it to treat anemia that results from chronic kidney disease or kidney failure. They may also give it to people with rare types of cancer.
If you have CKD or any anemia with low EPO, you may be able to boost your EPO levels with physical activity and dietary iron.
Regular, vigorous physical activity may cause your body to use more oxygen. Your brain then tells your body to create more EPO in response. Bicycling, jogging and swimming are some examples of activities that may cause you to use a lot of oxygen.
Advertisement
Iron is one of the main elements of hemoglobin. Hemoglobin helps carry oxygen to cells in your body. Good sources of dietary iron include:
Erythropoietin is an essential hormone that tells your bone marrow when to make more red blood cells. But sometimes, your body inappropriately produces too many or too few red blood cells. This can cause health problems. Your healthcare provider can order a blood test to see how much EPO you have in your blood and recommend the proper treatment.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
If you have a condition that’s affecting your kidneys, you want experts by your side. At Cleveland Clinic, we’ll work with you to craft a personalized treatment plan.
