Typhus is a group of bacterial illnesses that cause similar symptoms, like high fever, chills, rash, body aches, cough, digestive issues and confusion. Types include murine (endemic) typhus, epidemic typhus and scrub typhus. You get typhus from fleas, lice or chiggers. All types are treatable with antibiotics.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
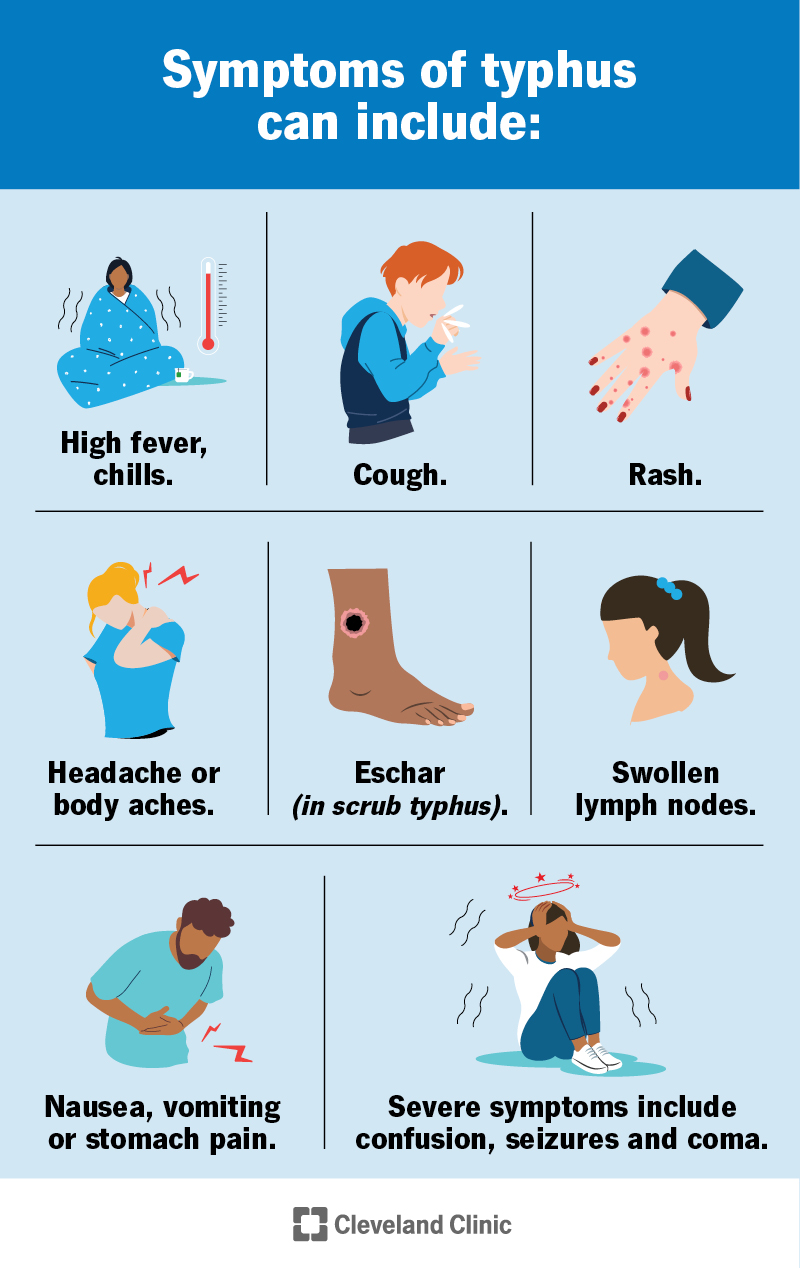
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/typhus)
Typhus (or typhus fever) is the name used for several different types of bacterial infections spread by bug bites that cause similar symptoms, like high fever and rash. These symptoms can be severe and lead to serious complications if left untreated.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Many people think typhus no longer exists, but you can still get it today. Historically, millions of people died from epidemic typhus outbreaks, usually during war, famine or other times of crisis. Today, it’s considered rare. On the other hand, millions of people worldwide still get sick with scrub typhus every year.
There are three types of illnesses commonly called typhus:
Symptoms of typhus can include:
Advertisement
*The rash usually appears a few days after other symptoms. It starts on your trunk and spreads to the rest of your body (except the palms of your hands and soles of your feet).
Symptoms are slightly different depending on the type of typhus. Not everyone experiences every symptom.
Video content: This video is available to watch online.
View video online (https://cdnapisec.kaltura.com/p/2207941/sp/220794100/playManifest/entryId/1_1soi4276/flavorId/1_5f3sgelj/format/url/protocol/https/a.mp4)
Learn the difference between typhoid and typhus.
Bacteria cause all three types of typhus:
Typhus spreads when a flea, louse (lice) or chigger carrying typhus bacteria bites you and their poop gets into the bite. Different types of bugs spread different types of typhus:
No, none of the three types of typhus are contagious (spread from person to person). But in crowded living conditions, lice can spread typhus bacteria from one person to another.
You’re at risk for typhus if you’re around fleas, body lice or chiggers in areas where they carry the bacteria that cause it.
Left untreated, typhus can lead to multiple complications, including:
If you get typhus in the early stages of pregnancy, you have a higher risk of miscarriage, preterm birth and low birth weight.
A provider usually diagnoses typhus based on your symptoms and whether you live in or have traveled to an area where you could’ve been infected. They may also get a blood test or test a sample of the skin around the eschar (biopsy). Make sure to tell your provider if you’ve traveled recently or could’ve been bitten by fleas, lice or chiggers — even if you don’t remember being bitten.
If your provider gets a blood test or biopsy, it can take several weeks to get the results. You may also need to get multiple blood tests over a few weeks. Your provider will need to treat you before they know whether the test is positive.
Advertisement
Yes, antibiotics can cure a typhus infection. Providers usually treat murine, epidemic and scrub typhus with doxycycline. If you’re pregnant or have other health conditions, your provider might prescribe a different antibiotic.
If you have typhus, expect to take antibiotics for three days to two weeks, depending on the type. If you don’t treat epidemic typhus, your symptoms could go away on their own, only to come back months or years later (Brill-Zinsser disease). Symptoms of Brill-Zinsser disease are usually milder than the initial typhus symptoms. It rarely causes complications. But lice can spread the infection to other people when your symptoms return.
When treated early with antibiotics, all types of typhus have a good prognosis (outlook). Murine typhus is rarely fatal. Mortality (death) rates for other types of typhus vary. But experts estimate around 10% to 30% of people die of epidemic and scrub typhus if left untreated.
See a healthcare provider if you have symptoms of typhus and you could’ve been bitten by fleas, lice or chiggers (even if you don’t remember being bitten). Let your provider know if you’ve traveled recently.
Call 911 (or your local emergency services number) or go to the emergency room if you experience symptoms of severe illness, including:
Advertisement
It might be helpful to ask your provider:
The best way to prevent typhus is to avoid flea, lice and chigger bites. Tips for avoiding bites include:
Advertisement
Yes, you can get typhus in the U.S. There are a few dozen reported cases each year. It’s most common in California, Texas and Hawaii.
Most of the time, bugs are simply annoying. But they can also spread diseases that can make you very sick. While typhus might be rare where you live, it’s still important to know the symptoms, how it spreads and where it’s most common. Talk to a healthcare provider if you have concerning symptoms or are wondering how to reduce your risk of flea, louse or chigger bites.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Need care fast? Cleveland Clinic’s Express Care and Urgent Care locations treat everything from sprains to sinus infections — no appointment needed.
