Telogen effluvium is a common type of hair loss that affects people after they experience severe stress or a change to their body. Symptoms include thinning hair, usually around the top of your head. Treatment exists to reverse hair loss, but hair will typically grow back in three to six months without treatment.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
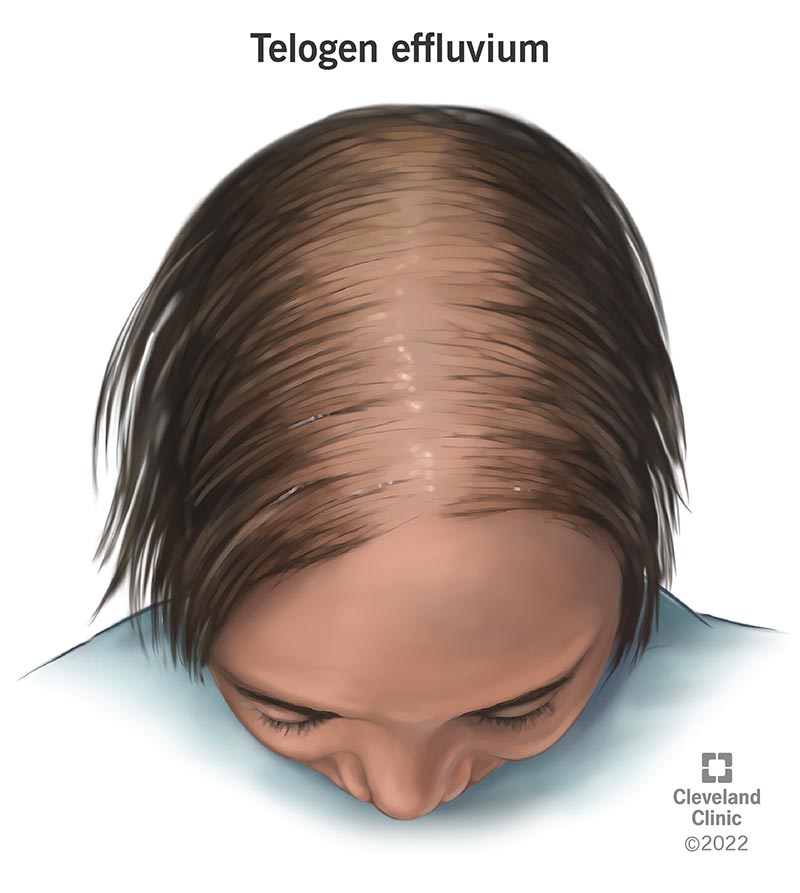
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/24486-telogen-effluvium)
Telogen effluvium is a type of temporary hair loss caused by a stressor or change to your body. Your hair has three stages of growth and loss (shedding):
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Telogen effluvium affects your hair when it’s in the telogen stage. After a stressor or change to your body, up to 70% of your hair in the anagen stage prematurely enters the telogen phase, which causes hair loss.
Acute telogen effluvium lasts fewer than six months, and your hair loss tends to happen two to three months after a stressor or change to your body. In 95% of cases, acute telogen effluvium goes away (resolves).
Advertisement
Chronic telogen effluvium lasts longer than six months. It affects your entire scalp and may not have a clear cause. You may lose your hair in handfuls during the early stages of chronic telogen effluvium, but it won’t cause total baldness.
Anyone can develop telogen effluvium. However, your chances of developing chronic telogen effluvium without a detectable cause increase if you’re a woman and are between 30 and 60 years of age.
Telogen effluvium is one of the most common causes of rapid hair loss. It’s also one of the most common causes of hair loss in women.
Telogen effluvium causes hairs to enter the resting stage from the growing stage prematurely. Most people who are healthy lose up to 100 strands of hair per day. If you have telogen effluvium, you may lose up to 300 strands of hair per day.
Telogen effluvium may affect the hair all over your scalp, but it most commonly appears on the top of your head rather than the back or sides of your head. It usually won’t affect your hairline or cause total baldness, but severe cases of telogen effluvium may affect other areas of your body, including your eyebrows and body hair. Occasionally, the hair-thinning can mimic male- or female-pattern hair loss. Telogen effluvium has heavy shedding and rapid loss. Male- and female-pattern hair loss has slow thinning.
Telogen effluvium won’t affect your physical health, but it can affect you psychosocially (how society and social groups affect your thoughts and emotions) and psychologically (how you think about yourself and your behavior). You may experience emotional stress, anxiety and depression.
Symptoms of telogen effluvium include:
If you have telogen effluvium, your scalp should look healthy. You shouldn’t have any other symptoms, such as a rash, itching, burning, pain or flaking.
The following factors may trigger telogen effluvium:
No, telogen effluvium isn’t contagious.
Telogen effluvium is easy to recognize. A healthcare provider can confirm it during a physical examination of your scalp. They may conduct a “pull test,” in which they gently pull a small clump of 40 to 60 hairs between their fingers. Under typical conditions, they may only pull two to three hairs from your scalp. If you have telogen effluvium, they may pull at least four to six hairs from your scalp with white bulbs at the roots.
Advertisement
Your healthcare provider will also ask you about your diet and recent medical history. They may identify a dietary cause or a stress or illness that occurred about three months before you noticed hair loss. In many cases, someone with telogen effluvium has fully recovered from a stressor or illness and doesn’t see a connection between it and their hair loss.
In most cases, your healthcare provider can diagnose telogen effluvium without any testing. They may recommend further testing, including blood tests or a scalp biopsy, if they suspect a condition or illness has caused telogen effluvium.
Because one of the main causes of telogen effluvium is a stressor on your body, it’s important to identify the cause. Once you address the cause, most cases of telogen effluvium will resolve without treatment within six to eight months.
Telogen effluvium should resolve on its own, so you may not need treatment. However, common telogen effluvium treatments may include:
Advertisement
Telogen effluvium usually lasts between three and six months.
Yes, your hair will grow back after telogen effluvium. After the three- to six-month shedding period, you’ll notice new hair growth in your affected areas.
Telogen effluvium can be stressful, and you may fear that you’ll lose all of your hair. However, if you have telogen effluvium, the outlook is good. It usually goes away three to six months after you start noticing your hair loss. Your healthcare provider can also help you take steps to promote new hair growth.
There are ways to help keep your hair healthy and promote hair growth, including:
Advertisement
Telogen effluvium is a type of hair loss that involves rapid shedding of hair over a short period. It typically happens a few months after your body goes through something physically or emotionally stressful. It can also result from sudden hormonal changes. Hair loss due to telogen effluvium is usually temporary, and your hair often grows back without treatment once you no longer have that stress.
Androgenic alopecia (male pattern baldness and female pattern baldness) is a type of hair loss that’s more gradual than telogen effluvium. It’s not known exactly what causes androgenic alopecia. Without medications or treatment, hair loss due to androgenic alopecia is permanent.
Telogen effluvium is a common condition that causes temporary hair loss anywhere on your body, but it usually affects your scalp. Its causes usually include a stressor or change to your body. It can be emotionally and mentally challenging, and you may fear that you’re going bald, but it’s important to remember that your hair will grow back in time.
Reach out to your healthcare provider as soon as you notice hair loss, especially if it causes additional stress.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Losing your hair can be shocking and overwhelming. At Cleveland Clinic, we’ll find the right treatment to help you feel (and look) like yourself again.
