A unicornuate uterus is a congenital irregularity where you only have one fallopian tube and an abnormally shaped uterine cavity. It's a rare condition that causes pregnancy complications. Certain variations cause pelvic pain. Your healthcare provider may recommend treatment depending on the type of unicornuate uterus you have.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
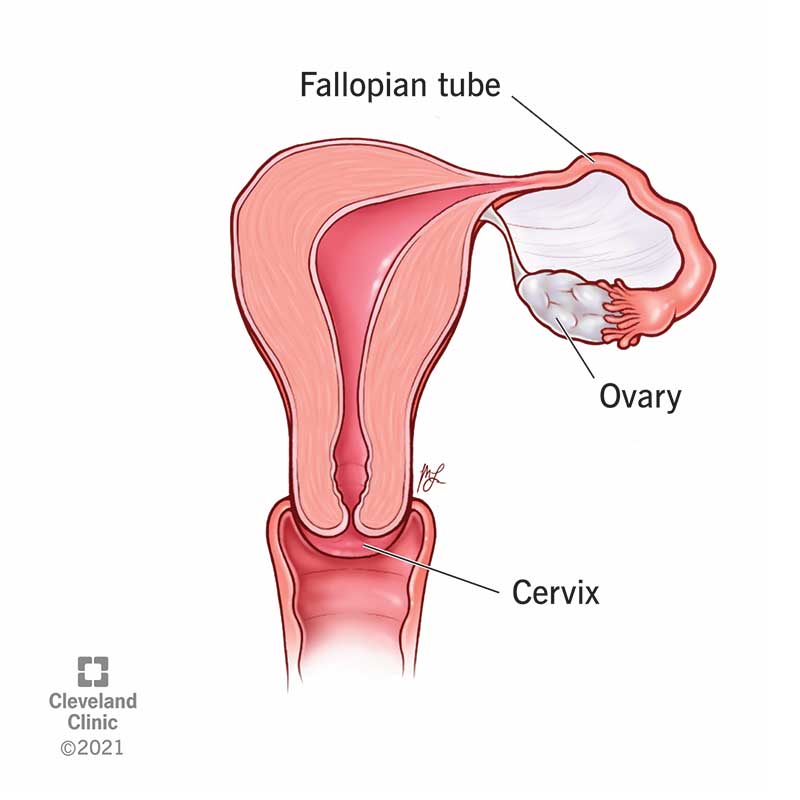
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/23302-unicornuate-uterus)
A unicornuate uterus is a rare condition that causes you to have only half a uterus. If you have a unicornuate uterus, you have one working fallopian tube (instead of two) and a smaller uterine cavity. It's a congenital uterine anomaly, meaning you were born with it. Your body reabsorbs the other half of your uterus.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
In a typical female, there’s one uterus with two connecting fallopian tubes. The hollow cavity of your uterus is where a baby grows. It looks like an upside-down pear. The horn-like fallopian tubes are located at the top and on either side of your uterus. A normal uterus almost has the appearance of a bull with two horns. Fallopian tubes are responsible for transporting eggs from your ovaries to the uterus during ovulation.
About 75% of people with a unicornuate uterus will have a rudimentary horn. A rudimentary horn is what’s left of the uterine tissue that was absorbed. The rudimentary horn may or may not be connected to the unicornuate uterus. In addition, the rudimentary horn may or may not have functioning endometrial lining/cavity.
Some people with a unicornuate uterus will have miscarriages or may have preterm delivery. When a unicornuate uterus is also associated with a rudimentary horn, a person can also experience pelvic pain. Other names for a unicornuate uterus are a single-horned uterus or a uterus with one horn.
It's rare to have a unicornuate uterus. Approximately 0.4% of the population has a unicornuate uterus. Of all the uterine abnormalities, it's one of the rarest.
Advertisement
Yes, having a unicornuate uterus can affect pregnancy. You can still have a baby if you have a unicornuate uterus, but you are at higher risk for miscarriage and preterm birth. For this reason, your healthcare provider will monitor you more closely. Often, a person finds out they have a unicornuate uterus after difficulty conceiving or repeat miscarriages.
Some people never know they have a unicornuate uterus. Others learn about the condition once they’re pregnant or during workup for infertility.
If your functioning rudimentary horn is connected to your uterus, you can be asymptomatic your whole life. This is because blood and can drain from the horn and flow through your vagina. When your rudimentary horn isn’t connected to your uterus and contains endometrium, there can be symptoms. This is because the menstrual fluid has nowhere to go and backs up inside the horn.
Signs of an obstructed rudimentary horn are:
A unicornuate uterus is a congenital abnormality that develops while you are still in the womb. It happens when the two Mullerian ducts don’t fuse together during development. One Mullerian duct develops into the smaller unicornuate uterus and the other Mullerian duct is reabsorbed by your body. In a typical uterus, the two ducts come together to create a uterus. Healthcare providers don’t know why the ducts do not join correctly for some people.
Having a unicornuate uterus can cause painful menstruation if you have a rudimentary horn that isn’t connected to the rest of your uterus. This horn can cause painful periods because the blood cannot flow through it and out of your vagina. However, if you have a connected rudimentary horn or no horn, you might not feel any menstrual pain.
Diagnosis starts with a physical exam and a discussion of your medical history. Typically, this includes a pelvic exam.
A unicornuate uterus is usually found only when you experience problems like recurrent miscarriages, trouble conceiving or painful periods. It's not usually detected during routine gynecological exams.
Your healthcare provider will use imaging tools like ultrasound, MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) or hysterosalpingogram (HSG) to diagnose unicornuate uterus.
There are different types of rudimentary horns that are associated with a unicornuate uterus:
Advertisement
In people with a unicornuate uterus, approximately:
Imaging tools are needed to diagnose a unicornuate uterus. These tools help identify any obstructions and the size and shape of your uterus and rudimentary horn. Only imaging tools can show uterine tissues and how the blood is flowing through your uterus.
These tests can help detect a unicornuate uterus:
The treatment for a unicornuate uterus depends on if there is a rudimentary horn, if the horn is connected to your uterus and if there’s endometrium inside a horn.
Most healthcare providers don’t recommend surgical intervention unless you’re having severe pain or a mass develops within a non-communicating rudimentary horn with an endometrial cavity. There’s a high risk of health complications in this type of rudimentary horn, especially if you become pregnant. This type of unicornuate uterus is known to cause pelvic pain since menstrual blood becomes trapped.
If you don’t have a rudimentary horn or your rudimentary horn doesn’t have functioning endometrial tissue, you likely won’t need treatment.
Advertisement
The goal of surgery is to remove a functioning rudimentary horn. This can eliminate pelvic pain as well as the chance that a pregnancy grows inside the horn, which would be life-threatening.
Surgery on a unicornuate uterus isn’t recommended. Its shape and appearance can’t be changed. But a functioning noncommunicating horn will be removed.
People with a unicornuate uterus experience more miscarriages. However, many people with a unicornuate uterus will have healthy pregnancies. The rate of miscarriage in people with a unicornuate uterus is about 35%. You’re also at higher risk for preterm birth and delivery via cesarean (c-section).
People who become pregnant and have a unicornuate uterus are at high risk for:
If a person becomes pregnant in their rudimentary horn, it can be potentially life-threatening. In a noncommunicating horn, there’s a high risk of uterine rupture due to lack of space.
If you have any type of unicornuate uterus, your healthcare provider will monitor you and your baby closely during pregnancy. You’ll likely have more appointments and more ultrasounds. Medications may be used to reduce your chances of preterm delivery.
Advertisement
If you have a unicornuate uterus, you are more likely to have a c-section. This is because your baby is likely to be in a breech position due to a lack of space within your uterus. If your baby is breech, it means they are feet or bottom first in your uterus instead of head first.
It's possible to carry twins if you have a unicornuate uterus. This would be extremely high risk, as the shape and size of the uterus aren’t ideal for two babies. Since many people with a unicornuate uterus struggle with infertility, IVF (in-vitro fertilization) is common. Carrying multiples is a known health risk associated with IVF.
A unicornuate uterus is congenital and formed when you were still developing in the womb. Most of the time, a person doesn't know they have a unicornuate uterus until they’re pregnant or trying to become pregnant. There is nothing you can do, or your mother could have done to prevent a unicornuate uterus.
There’s a link between renal agenesis and a unicornuate uterus. Renal agenesis is when you’re missing one kidney at birth. The renal anomaly is usually found on the same side as the rudimentary horn. Researchers aren’t entirely sure why this happens. Having a unicornuate uterus also puts you at higher risk for endometriosis if you have an associated obstructed rudimentary horn.
If you have a unicornuate uterus, it's natural to have questions for your healthcare provider. Some common questions are:
Hearing you have a unicornuate uterus can be difficult. Speak with your healthcare provider to make sure you know how to best care for yourself and minimize health risks from this condition. Also know that people with a unicornuate uterus can become pregnant and have healthy babies.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
From routine pelvic exams to high-risk pregnancies, Cleveland Clinic’s Ob/Gyns are here for you at any point in life.
