Anal yeast infections are a common fungal infection caused by a yeast called Candida. Symptoms include an intense itching sensation around your anus called pruritus ani. Treatment includes antifungal creams, ointments or suppositories. You can prevent anal yeast infections by keeping your perianal area clean and dry.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
A yeast infection can occur almost anywhere in and on your body. An anal yeast infection is a yeast infection in your anus and the area around your anus (perianal area). A yeast infection anywhere on your skin is called candidiasis. Candidiasis is a fungal infection caused by a yeast called Candida.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Your skin has a natural balance of yeast and bacteria. The bacteria help prevent the overgrowth of yeast on your skin. But sometimes your body’s natural balance of yeast and bacteria gets disturbed. When this happens, Candida can grow out of control. When there’s an overgrowth of Candida, it can dig below the surface of your skin, causing a yeast infection.
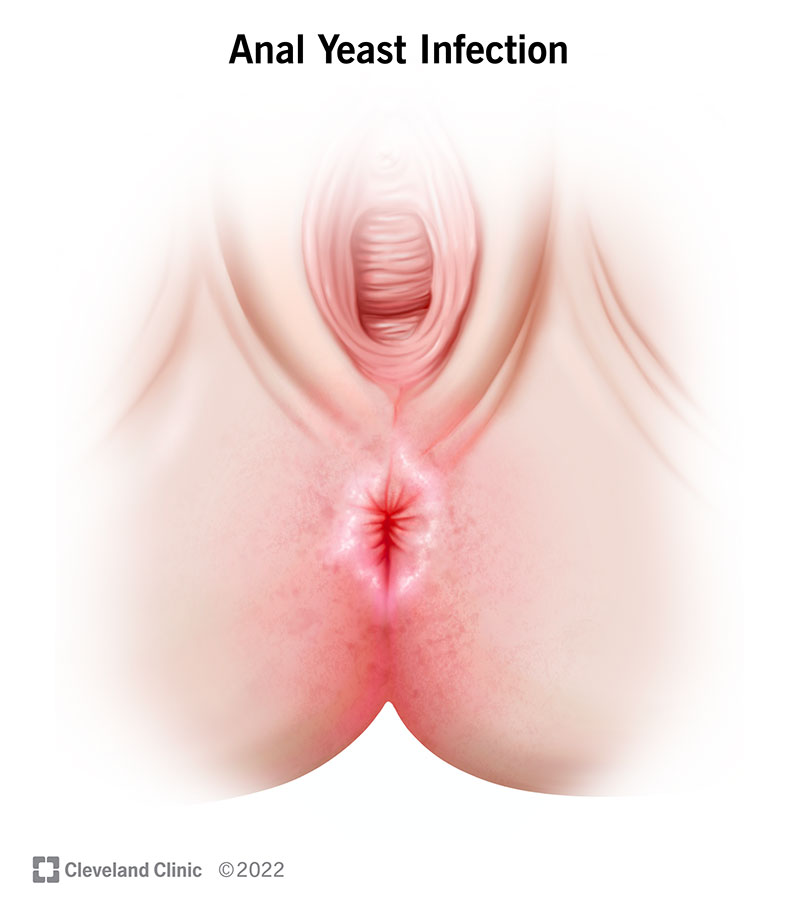
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/22907-anal-yeast-infection)
The first sign of an anal yeast infection is intense anal itching. A persistent itchy sensation on the skin around your anus is called pruritus ani. Pruritus ani is a common skin condition. Other symptoms of an anal yeast infection may include:
An anal yeast infection can easily spread to your penis or vagina. So you may notice other symptoms in those areas.
A yeast called Candida causes anal yeast infections. Some Candida normally live in your gastrointestinal tract. A buildup of Candida in your intestines can travel to your anal canal, causing a yeast infection.
Candida also grow and thrive in warm, damp environments. Conditions and other factors that allow Candida to grow include:
Advertisement
Yeast infections are more common in certain groups of people. This includes people who:
Yeast infections are also more common in people with weakened immune systems. This may be because of a condition such as diabetes. Or it may be due to the use of a medication that suppresses your immune system.
An anal yeast infection isn’t considered a sexually transmitted infection (STI). But a person with an anal yeast infection can transfer the infection through unprotected anal sex.
Your healthcare provider can diagnose an anal yeast infection through a physical examination. They'll ask you about your symptoms and look at your perianal area.
Your healthcare provider may want to collect a sample for testing. They may use a tongue depressor or scalpel to gently scrape some of the skin from your perianal area. A pathologist will look at the sample under a microscope to confirm the type of fungus that’s causing the infection. They may place the sample in a culture. The sample will grow in the culture so the type of fungus can be determined.
Treatment for an anal yeast infection may include an antifungal medication. Many of the same antifungal medications used for vaginal yeast infections can be used for anal yeast infections as well. Your healthcare provider may recommend an antifungal cream, ointment or suppository. You can buy many antifungal medications over the counter. Your healthcare provider may prescribe a stronger antifungal medication if necessary. Antifungal medications include:
You may be able to get rid of an anal yeast infection with home remedies. Home treatment options haven’t been researched as thoroughly as FDA-approved antifungal medications. But scientists have performed some small studies. You should ask your healthcare provider before trying any home treatment remedies. Home treatment options may include:
Make sure to keep your perianal area clean and dry while treating your yeast infection. Keeping the area clean and dry can also help prevent infections from returning in the future.
Advertisement
You may be able to cure an anal yeast infection at home with an over-the-counter antifungal medication. But if the infection persists and doesn’t go away within a couple of weeks, call your healthcare provider. You may need a prescription treatment option.
An anal yeast infection may take some time to cure. After you start antifungal treatment, the infection should start to clear up within a week or two. But yeast infections can be hard to treat. If your symptoms persist, call your healthcare provider.
You can prevent an anal yeast infection by keeping your perianal area clean and dry. Other steps you can take to prevent anal yeast infections include:
An anal yeast infection can be extremely itchy and unpleasant. But the good news is, it’s usually easy to treat. You can use antifungal medication such as creams, ointments and suppositories. You can prevent anal yeast infections by practicing good bathroom hygiene. And make sure to keep your perianal area clean and dry. If this is your first yeast infection or you’re getting them repeatedly, call your healthcare provider. They’ll be able to determine the most appropriate treatment option for you.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Need care fast? Cleveland Clinic’s Express Care and Urgent Care locations treat everything from sprains to sinus infections — no appointment needed.
