Chronic hives (chronic urticaria) are red, itchy skin welts that last more than six weeks. Many people have these welts every day for a year or longer. People with certain autoimmune diseases are more prone to chronic hives. But often, the cause of chronic hives is unknown. Antihistamines, steroids and immunosuppressants can soothe the hives.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
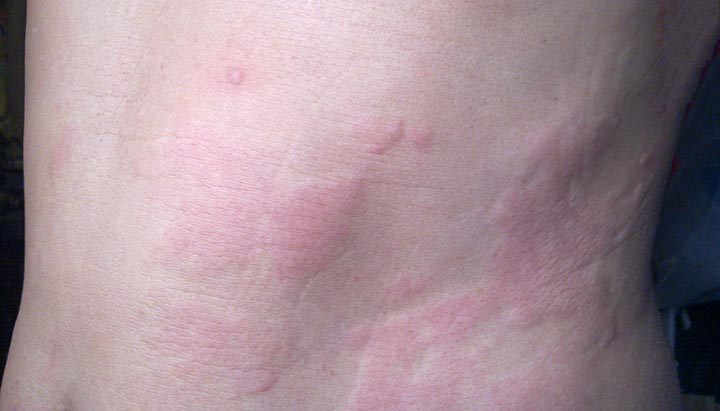
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/22900-chronic-hives)
Chronic hives are itchy, raised, red bumps or welts that appear on your skin at least twice per week. These welts, also called wheals, are chronic when they last more than six weeks.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
You may hear this condition called chronic idiopathic urticaria:
Hives (urticaria) and angioedema (swelling) can occur together. Hives are raised red bumps or splotches on your skin. Angioedema (swelling) may occur in deep layers of tissue. This swelling can affect your face, lips, throat, hands, feet and genitals.
Chronic hives are different than acute hives:
Up to 5% of people develop chronic hives. The condition can affect anyone, but is more common in women ages 30 to 50.
For most people with chronic hives, there’s no known cause. Rarely, medication allergies or food allergies cause chronic hives. The most common allergic cause is something you consume on a regular basis. Other types of allergies may also bring on chronic hives.
Advertisement
Some people develop chronic hives when their body changes temperature rapidly due to heat, cold or physical activity. Pressure on your skin from tight clothing may also cause the condition.
About 1 in 5 people who develop chronic hives also have an autoimmune disease, such as:
Other conditions that may cause chronic hives include:
Hives can appear anywhere on your body and look different on each person. Hives can have different shapes and sizes. They may be as small as a pinprick or larger than a softball.
Chronic hive symptoms include:
Healthcare providers who diagnose and treat chronic hives include:
Your healthcare provider can diagnose chronic hives by examining your skin and learning more about your symptoms.
Diagnostic tests for chronic hives can pinpoint or rule out causes. You may get one or more of these tests:
Treatments for chronic hives include:
Advertisement
You can try these steps at home to ease itchy skin and soothe inflammation:
For half of people with chronic hives, the hives go away (often without treatment) within a year. Treatments can ease symptoms of long-lasting hives.
Video content: This video is available to watch online.
View video online (https://cdnapisec.kaltura.com/p/2207941/sp/220794100/playManifest/entryId/1_slrzqrkk/flavorId/1_5f3sgelj/format/url/protocol/https/a.mp4)
The unpredictability of chronic hive flares can take a toll on your mental health. Learn tips to help manage the impact.
Call your healthcare provider if you experience:
You may want to ask your healthcare provider:
Stress and anxiety can worsen skin diseases. Anti-anxiety medicines may help. You may also benefit from stress-relieving therapies like mindfulness or meditation.
Chronic hives (chronic urticaria) can be itchy and uncomfortable. You may become self-conscious about your appearance. Most of the time, providers can’t pinpoint the cause of chronic hives. However, treatments like antihistamines, steroids and even immunosuppressants can help. You can also take steps at home to ease itching and swelling. For many people, chronic hives eventually go away, although it may take a year or longer.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Every day, people see your skin, hair and nails. At Cleveland Clinic, our expert and caring dermatology team will make sure they’re healthy and strong.
