Pityriasis rosea is a common condition that causes discolored patches on your skin. A virus may cause pityriasis rosea, but experts aren’t sure. For most people, it resolves without treatment. Some treatments can alleviate related symptoms, including itching.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
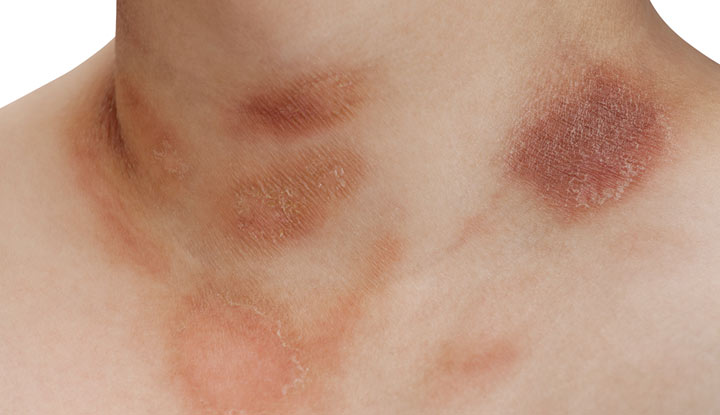
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/17729-pityriasis-rosea-802333962)
Pityriasis rosea (pih-tuh-RY-uh-sis ROH-zee-uh) is a common skin condition that causes patches of your skin to develop raised, scaly rashes. It may appear on any part of your body, but it usually appears on the trunk (torso), arms and legs. “Pityriasis” means “scaly,” and “rosea” means “pink,” but the rashes may look red, gray, brown or purple.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Pityriasis rosea is also known as Christmas tree rash.
Anyone can get pityriasis rosea. You may be more likely to develop it if you’re:
In some cases, people with pityriasis rosea report that they had significant or long-term stress before developing a rash. However, there isn’t enough research to determine that stress may cause pityriasis rosea.
Pityriasis rosea doesn’t usually affect people over the age of 60. However, if it does, the symptoms may last for a longer period.
Pityriasis rosea commonly affects the skin on your trunk, arms or legs. A variant called inverse pityriasis rosea can affect the skin on your neck, face, armpits (axillae) and groin, though it isn’t common.
Your skin may develop discolored patches (lesions) that look like scales or dry, crinkly paper. The patches may itch.
The symptoms of pityriasis rosea usually develop in stages:
Advertisement
Pityriasis rosea doesn’t hurt. However, if you scratch your patches, you may break your skin, leading to an infection that can cause pain.
Healthcare experts believe herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6), HHV-7 and/or HHV-8 cause pityriasis rosea, but there aren’t any conclusive studies. These strains of the herpes virus aren’t related to the strains that cause cold sores or genital herpes.
Studies show that some skin conditions may appear with COVID-19, including pityriasis rosea. However, the studies don’t conclusively prove that COVID-19 causes pityriasis rosea.
Pityriasis rosea and ringworm look similar. They’re both papulosquamous (pap-you-lo-skway-miss) disorders, which is a term used to characterize skin disorders according to the presence of raised, discolored, scaly patches of skin.
However, a fungus causes ringworm. No one knows what causes pityriasis rosea, though healthcare experts think a virus might be responsible.
Pityriasis rosea isn’t a sexually transmitted disease or infection (STD or STI). You can’t spread pityriasis rosea to another person through unprotected sex or skin-to-skin contact.
If you develop symptoms of pityriasis rosea while pregnant, contact your healthcare provider right away. Studies show that the development of pityriasis rosea during pregnancy may cause birth complications, including miscarriage and poor muscle tone and development once the baby is born (neonatal hypotonia).
Your healthcare provider can typically diagnose pityriasis rosea after a physical exam. However, pityriasis rosea can look similar to other skin conditions, including:
If there’s any doubt, your healthcare provider may perform the following tests:
In most cases, pityriasis rosea goes away without any treatment in six to eight weeks.
If you have a very itchy rash, your healthcare provider may prescribe the following to help relieve your symptoms:
Advertisement
There are several over-the-counter products or home remedies that can help stop your rash from itching.
While home remedies are safe for most people, it’s a good idea to check with your healthcare provider before trying some of the following options. You may be at risk of developing an allergic reaction on your skin.
If you have pityriasis rosea, you don’t have to avoid any foods or drinks. However, some people believe that eating an anti-inflammatory diet may relieve itching. Some research shows that people who follow a Mediterranean diet have lower levels of inflammation in their bodies.
Advertisement
Foods that have anti-inflammatory properties include:
Foods that may increase inflammation include:
If you have pityriasis rosea, it can generally be well-managed without any treatment. It should clear your body in six to eight weeks. However, if you experience any symptoms, therapy can provide relief.
If you have pityriasis rosea, it’s unlikely that you’ll get it again. You also won’t have permanent scarring or other damage to your skin.
There isn’t any way to prevent pityriasis rosea.
Call your healthcare provider if:
Advertisement
Though pityriasis rosea is a common skin rash, it can still make you feel self-conscious, and it can be unpleasant if it itches. There isn’t a cure, but it isn’t contagious. Once it’s gone, you likely won’t develop it again.
It’s important to pay attention to your skin. Contact your healthcare provider as soon as you notice a rash.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Every day, people see your skin, hair and nails. At Cleveland Clinic, our expert and caring dermatology team will make sure they’re healthy and strong.
