Sebaceous glands are microscopic glands found in your hair follicles that secrete sebum. Sebum is an oily substance that protects your skin from drying out. Sebaceous glands can clog, so you can keep your glands healthy by following a skin care routine that includes cleansing and moisturizing your skin.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
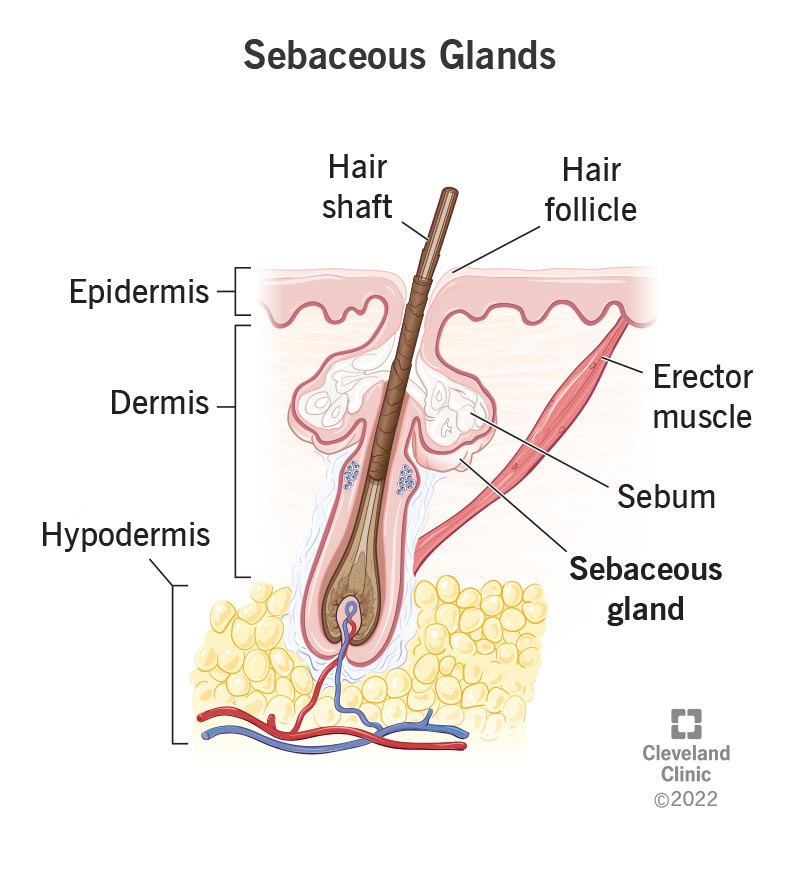
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/24538-sebaceous-glands)
Sebaceous glands are an organ in your skin that make and secrete sebum. Sebum is a substance that provides a protective coating for your skin to help it retain moisture. Most of your sebaceous glands connect to your hair follicles.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
There are two types of sebaceous glands. Both types have different locations on your body.
The majority of your sebaceous glands have openings attached to your hair follicles. Some sebaceous glands work with your sweat glands and open at the surface of your skin instead of at your hair follicles. Both types perform the same function, which is to create and release sebum.
Sebaceous glands are responsible for producing and secreting sebum. Sebum is an oily substance made up of fat molecules (lipids) that include:
Sebum is a natural lubrication that protects your skin from:
Sebum also contributes to your body odor.
After you’re born, your sebaceous glands activate and start producing sebum. The amount of sebum your body produces is slow through childhood until you reach puberty. At the time of puberty, your body produces excessive amounts of sebum. Your sebum production reduces to normal amounts during adulthood. After age 70, your body’s sebum production slows down gradually.
Advertisement
Sebaceous glands develop on or near your hair follicles in the second layer of your skin (dermis). You have thousands of sebaceous glands all over your body. The only place where you don’t have sebaceous glands are on the palms of your hands and the soles of your feet. You have the most sebaceous glands on your face and scalp. Sebaceous glands that aren’t attached to your hair follicles are common on your penis, labia, lips or inside of your nose.
If you hold a penny between your pointer finger and your thumb with the face pointing toward yours, the shape of your finger and thumb look like the outline of a sebaceous gland. The penny is the opening of the sebaceous gland, which is where your gland secrets sebum into your hair follicle. Inside the sebaceous gland are several cells that create sebum (epithelial cells).
Sebaceous glands are microscopic. To get an idea of the size of your sebaceous gland, look at a single strand of hair on your forearm. Below the surface of your skin is a tube where your hair grows. This is called your hair follicle. Inside of that tube is a tiny opening where your sebaceous gland releases sebum.
There are several conditions that can affect the health and function of your sebaceous glands. Some of the most common include:
Although most sebaceous glands don’t have any symptoms, signs and symptoms vary for each condition and could include:
Advertisement
A visual examination of your skin by your healthcare provider can diagnose sebaceous gland conditions, but they might offer additional tests to rule out conditions with similar symptoms or to confirm a diagnosis. Tests to check the health of your sebaceous glands include:
Treatment options vary for each condition and could include:
You can keep your sebaceous glands healthy and prevent clogging of your hair follicles and glands by using:
You can also help your sebaceous glands stay healthy by staying hydrated and drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
Advertisement
Both sebaceous glands and sweat glands are organs in your body that protect your skin from becoming too dry. Sebaceous glands produce an oily substance called sebum and sweat glands produce a watery substance called sweat. Sweat glands have ducts, which are pathways to excrete substances to the surface of your skin. Sebaceous glands secrete sebum through your hair follicles and don’t have ducts.
No. The glands in your breasts are mammary glands. Mammary glands are responsible for lactation or milk production.
Retinoids, like tretinoin (Retin-A®), are chemicals that use vitamin A. These chemicals are found in common skin care medications to treat several conditions like acne. Studies show that using retinoids shrinks the size of your pores, but they don’t shrink the size of your sebaceous glands. Retinoids also reduce your sebaceous glands’ production of sebum.
Sebaceous glands are an important organ for your body to keep your skin moisturized. It might be frustrating to have greasy hair or oily skin, but those are signs that your sebaceous glands are working. Follow a daily skin care routine to prevent your pores and hair follicles from clogging with excess sebum.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s primary care providers offer lifelong medical care. From sinus infections and high blood pressure to preventive screening, we’re here for you.
