A penile implant restores your ability to get an erection. There are two types of penile implants: inflatable and non-inflatable. Risks include erosion and mechanical failure. Most people can resume sexual activity six weeks after receiving a penile implant.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
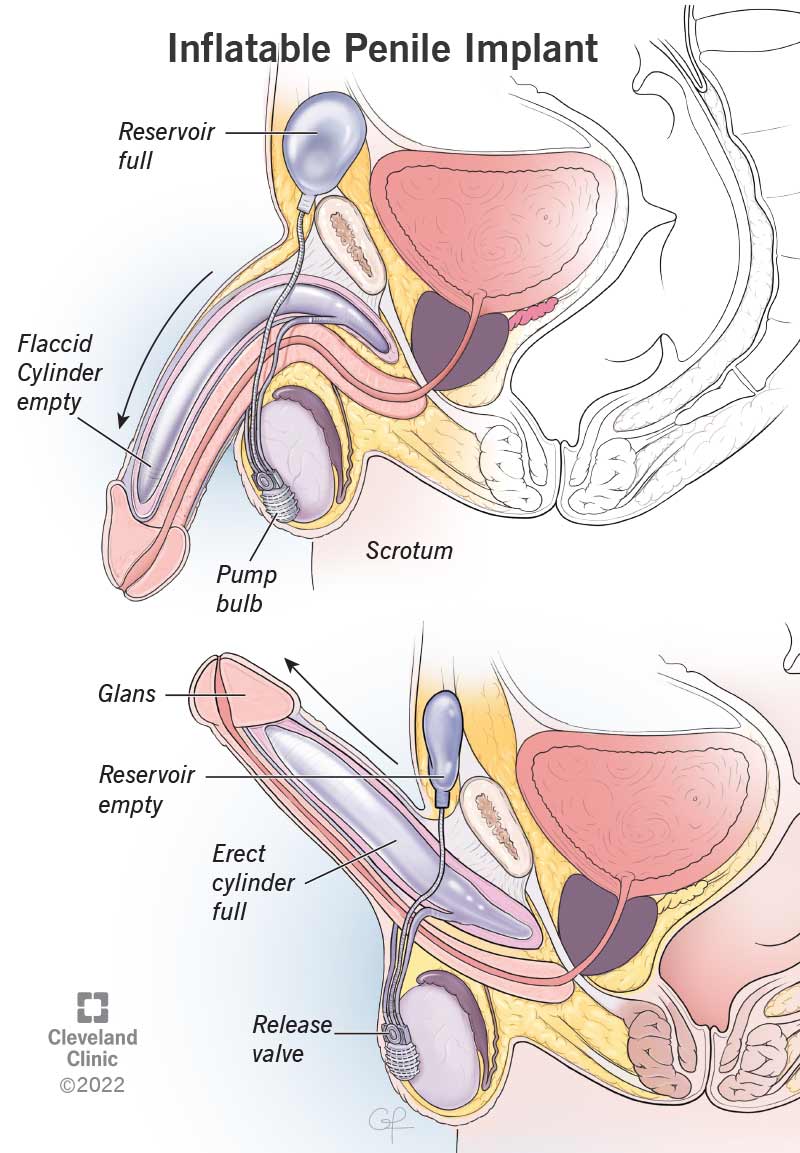
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/10054-penile-implants)
A penile implant is a surgically implanted device that helps you get an erection, usually if you have erectile dysfunction (ED).
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
There are two types of penile implants:
Other names for a penile implant include penis implant and penile prosthesis.
An inflatable penile implant consists of two cylinders, a reservoir and a pump that a healthcare provider surgically places in your body.
The provider inserts the cylinders into your penis. Tubes connect the cylinders to a separate reservoir under your lower abdominal (stomach) muscles. The reservoir contains fluid. A pump also connects to this system. It sits under the loose skin of your scrotum, between your testicles.
To inflate the implant (prosthesis), you press the pump in your scrotum. Pressing the pump doesn’t put any pressure on your testicles. The pump transfers fluid from the reservoir to the cylinders in your penis, inflating them to the level of hardness that you want. Once erect, you can maintain your erection for as long as you wish, even after an orgasm. When you want to stop being erect, pressing a valve on the pump returns the fluid to the reservoir, which deflates your penis.
Advertisement
A non-inflatable penile implant consists of two firm, flexible silicone rods. This type of device doesn’t require pumping. To use the implant, you press on your penis to extend the rod into position. You can use the implant for as long as you wish — the hardness doesn’t change, even after an orgasm. After using the implant, you press on your penis again to push it back down.
Most people who are good candidates for a penis implant have ED or Peyronie’s disease. However, their condition can’t improve naturally or with other conservative medical treatments, such as medications or a vacuum constriction device (penis pump).
A penile implant occurs after surgery to construct a penis (metoidioplasty or phalloplasty).
Penile implants are becoming more common. Worldwide, healthcare providers performed over 63,000 penile implants between 2005 and 2012. About 86% of those procedures occurred in the United States.
On average, penile implants last 20 years. When the implant wears out, it stops working. Your surgeon can revise it, usually by replacing it with a new implant.
Penile implants can’t make your penis bigger than it is before surgery. Your erection may even seem shorter than what you remember when you were getting natural erections.
It’s important to know that the head of your penis (glans) doesn’t get hard (engorged) after inflation because the implant isn’t in the head of your penis. This can make it seem like your penis isn’t as large as it was before your implant. Your healthcare provider may prescribe you a medication to help increase the blood flow to the head of your penis.
Modern penile implant models have cylinders that may slightly increase your penis length, thickness and stiffness. This can occur gradually over time as you use the device.
In most cases, the look and size of your erection after a penile implant are comparable to the size of your stretched-out penis before surgery. Your surgeon always measures the inside of your penis and places the biggest implant that’s safe to put in your body. The implant is a custom fit according to your inner measurements.
Yes, a penile implant allows you to get an erection whenever you’d like. It can take a couple of minutes to pump the inflatable penile implant to its full rigidity. The non-inflatable implant is always the same hardness.
Once you have a penile implant, you’ll always need the implant to get hard. Medications will no longer work. You won’t be able to get a natural erection without the implant, especially if a surgeon removes the implant and doesn’t replace it with another.
Advertisement
When you inflate your penis, the prosthesis makes your penis stiff and thick, like a natural erection. Most people with a penile implant report that sex feels the same or better than before the procedure. It won’t change the sensation on the skin of your penis. A penile implant also doesn’t affect your ability to ejaculate and orgasm. It may take you a few weeks or even a couple of months to adjust to the sensation of having an implant. However, many people who get penile implants report high satisfaction once they fully heal.
If you feel the implant with your own hand, you’ll be able to feel the difference, especially if it isn’t erect. However, during intercourse, your partner won’t be able to tell the difference between a penile implant and a natural erection.
Once you heal after surgery, the implant isn’t obvious to anyone else who might see you naked, such as in a locker room or public bathroom.
Video content: This video is available to watch online.
View video online (https://cdnapisec.kaltura.com/p/2207941/sp/220794100/playManifest/entryId/1_s1dn41d6/flavorId/1_5f3sgelj/format/url/protocol/https/a.mp4)
A penile implant restores your ability to get an erection. There are two types of penile implants: inflatable and non-inflatable.
Before a penis implant, you’ll meet with a healthcare provider. They’ll check your general health and take your vitals (temperature, pulse and blood pressure). They’ll also make sure that you can empty your bladder and don’t have any severe urinary issues. Once you meet with a surgeon, they’ll talk to you about which type of penile implant is right for you according to your body and your needs.
Advertisement
Tell your healthcare provider about any prescription or over-the-counter (OTC) medications you’re taking. These include herbal supplements. Aspirin, anti-inflammatory drugs, certain herbal supplements and blood thinners can increase your risk of bleeding. Be sure to check with your healthcare provider before stopping any medications.
Tell the healthcare provider about any allergies you have as well. Include all known allergies. These include medications (especially antibiotics), skin cleaners like iodine or isopropyl alcohol, latex and foods.
The healthcare provider will also give you specific instructions on eating and drinking before your penis implant. You shouldn’t eat or drink anything after midnight the night before your surgery. If you must take medications, you should take them with a small sip of water.
It’s a good idea to thoroughly wash your abdomen and groin the day before and the morning of your procedure to reduce the risk of infection. You don’t need to shave your abdomen or pubic hair around your penis and scrotum before your procedure. Your surgeon will do this immediately before your surgery.
If you have an active skin or urinary infection before surgery, notify your surgeon. Skin and urinary infections increase the risk of infecting your implant. Always make sure that you have no active infections in your body before having implant surgery.
Advertisement
A special team of healthcare providers will perform a penis implant. The team typically includes:
The anesthesiologist will sedate you (put you under) with general anesthesia. You won’t be awake, won’t move and won’t feel any pain during the procedure.
The urologist may insert a catheter into your bladder through your penis. A catheter is a soft, hollow tube that allows urine (pee) to flow out of your body. Your urologist will usually remove a catheter after the surgery.
The urologist will inject pain medication to keep you numb even after the procedure ends. The urologist will then make an incision on your genital area and insert the implant into your corpora cavernosa. Your corpora cavernosa (singular: corpus cavernosum) are two columns or tubes of spongy tissue that fill with blood and make your penis hard. Your healthcare team will customize the size of your implant according to the size of your penis.
If you get an inflatable implant, your urologist will then insert the reservoir in your abdomen and the pump inside your scrotum. They may or may not need to make additional incisions in order to place these components, but the incisions are quite small.
After inserting the implant, your surgeon will close the incisions with dissolvable stitches. They may stitch small silicone tubes (surgical drains) in your incision sites. These surgical drains remove blood or fluid from inside your body. They’ll then place a bandage over the incision.
A penis implant usually takes one to two hours to complete.
The anesthesiologist will stop putting anesthesia into your body. You’ll be conscious (awake) within a few minutes, but you’ll likely feel very groggy.
You’ll then move to a recovery room. Healthcare providers will wait for you to wake up more fully and track your overall health. Once you fully wake up, your groin and abdominal area may feel sore. Providers will treat your pain and teach you pain management techniques. They may also prescribe antibiotics.
In most cases, you can go home a few hours after a penile implant. However, you must have a family member or friend drive you home. It’s also a good idea to have a family member or friend help take care of you the first day or two after a penile implant.
The main advantage of a penile implant is that it allows you to get and maintain an erection firm enough for sex, whenever you wish and for as long as you want. It won’t change the sensation on the skin of your penis or your ability to orgasm and ejaculate.
Other advantages of a penile implant include:
An inflatable penile implant isn’t noticeable. You may have small scars from your incisions, but the scars usually aren’t noticeable.
Non-inflatable penile implants are always semi-erect, so they may be more difficult to obscure with clothes.
Penile implant surgery is overall very safe. However, it’s important to know about some of the uncommon risks, including:
It’s important to remember that your body is unique, so healing times vary among people. In general, pain, swelling and discomfort should decrease after a week. You may have tenderness for up to six weeks.
Your healthcare provider may prescribe antibiotics, pain relievers or other medications. Take them as directed.
To manage pain, some people take over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as aspirin (Bayer®), ibuprofen (Advil®) or naproxen (Aleve®). Not everyone can take NSAIDs, so be sure to ask your healthcare provider for other medications if needed.
To help your body heal as you recover, gently clean and dry your affected areas regularly to prevent infection. Wash your hands with soap and water before changing your bandages. It’s also a good idea to wash your hands before using the restroom.
To help reduce pain and swelling, apply an ice pack to your affected areas for up to 10 minutes. You may do this repeatedly throughout the day.
As you recover, it’s important to avoid heavy lifting or strenuous exercises that can put pressure on your incisions.
Your surgeon will let you know when it’s safe to resume masturbation or intercourse depending on your specific surgery. In general, avoid sexual activity for at least four weeks after a penile implant.
If you work at a desk, you should take at least a week off work.
If you have a more physically demanding job, you should schedule at least two to four weeks to recover before returning to work.
Schedule regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider.
If you have a surgical drain, your provider will typically remove it one to three days after the procedure.
You should then see a provider about four to six weeks after your procedure to learn how to use your penile implant.
Call a healthcare provider right away if you have any complications after a penile implant. These may include:
The cost of a penile implant is usually between $12,000 and $20,000. However, the price varies between surgeons and medical facilities. Talk to a healthcare provider to better understand their exact pricing.
Yes, insurance coverage for a penile implant is often applicable if a healthcare provider diagnoses you with erectile dysfunction. Many major insurance companies, Medicare and Medicaid cover the cost of surgery for people who are eligible.
Getting a penile implant is a personal decision. Talk to a healthcare provider to discuss your options if you wish to restore your ability to get and maintain an erection. A penile implant can boost your self-confidence and help restore your sex life, but you should be aware that a penile implant lasts around 20 years. You may need to get a new implant later on in your life. Talk to a healthcare provider about concerns, and learn more about what’s best for you and your health.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
When something’s wrong with your penis, you’ll want to get care right away. Cleveland Clinic’s experienced urology providers are here for you.
