A speech impairment, sometimes called a speech impediment or speech disorder, is a condition that makes it hard for you to communicate. There are many types and anyone can develop one. In some cases, children are born with conditions that affect speech. Other times, people have conditions or injuries that affect speech. Speech therapy can help.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
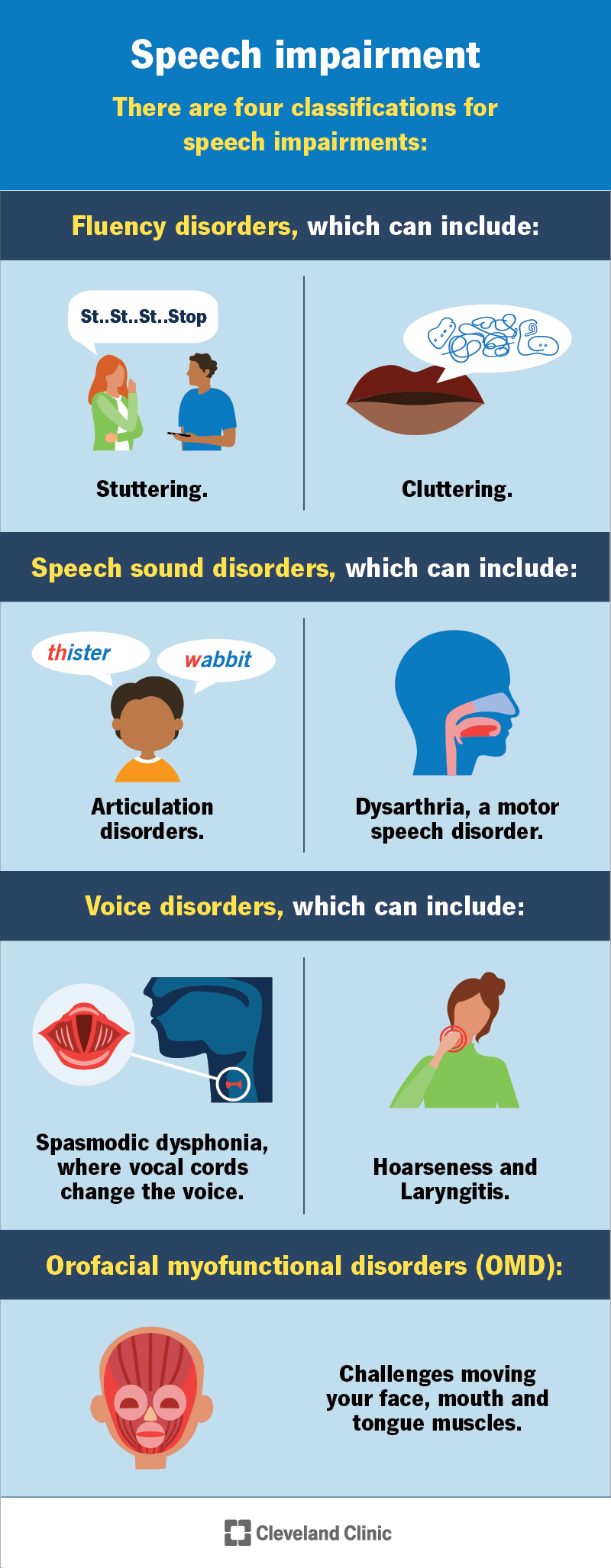
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/Images/org/health/articles/speech-impairment)
A speech impairment (sometimes called a speech impediment or speech disorder) happens when you have trouble saying sounds so that people don’t understand what you’re saying. Some people are born with conditions that affect their speech. But you can develop a speech impairment at any time in your life if you’re injured or have a medical condition that affects your voice or your ability to speak.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Without treatment, children with speech impairments may have difficulty learning to read and write. Research suggests children with speech impairments may develop mental health issues like anxiety and depression. Adults may feel anxious about trying to communicate and develop social isolation that can lead to depression.
There are different classifications for speech impairments:
Fluency is the flow of a person’s speech. A person is fluent when they speak continuously and smoothly. A fluency disorder involves chronic and repeated interruptions to speech flow. Examples of fluency disorders are:
An orofacial myofunctional disorder is when something affects how you use or move your face, mouth and tongue muscles. OMDs may affect how you speak, making it hard for you to make sounds like “s” as in sun or “sh” as in ship.
A speech sound disorder affects your ability to say sounds clearly. Examples of speech sound disorders are:
Advertisement
Some voice disorders may affect your ability to speak. Examples include:
Experts estimate that 5% of children in the U.S. ages 3-17 have a speech impairment that lasts for a week or longer. By the time children are in first grade, 5% have noticeable issues. About 2% of children in the U.S. have voice disorders that affect their ability to speak.
The overall picture is less clear when we’re talking about adults who have speech impairments. In adults, speech impairments are often classified by the specific condition.
For example, more than 3 million people in the U.S. stutter, or about 10% of the total U.S. population. While most people outgrow stuttering during their childhood, 1 in 4 people experience stuttering as adults. Voice disorders affect 4% of adults in the U.S.
Speech impairment symptoms vary depending on the cause. For example, if you have stuttering, you can’t control the muscles that you use to speak, so you repeat sounds or syllables, or hold or draw out certain sounds or syllables. If you have a voice disorder, your voice may sound uneven or shaky, strangled or breathy.
Healthcare providers don’t know all the reasons why children and adults have speech impairments (sometimes called speech impediments). In general, anything that may cause brain damage or nerve damage may affect your ability to speak, such as:
Healthcare providers usually begin diagnosis with a comprehensive physical examination. A pediatrician may do a developmental evaluation. A provider or pediatrician may refer you or your child to a speech-language pathologist (SLP), a specialist who diagnoses and treats conditions that affect your ability to communicate.
Treatment varies depending on your situation. For example, speech therapy is a common treatment for many speech impairments (speech disorders). If you have a voice disorder that affects your speech, your provider may refer you to specialists for voice therapy.
In some cases, yes, speech therapy can help people overcome speech impairments. But everyone is different. You can develop a speech impairment if you have an underlying condition that affects your ability to speak. In that case, speech therapy may help, but it may not fix the issue.
Advertisement
There are many types of speech impairments, which makes it hard to say exactly what you can expect. For example, some speech impairments improve as children grow older. If a medical condition causes speech issues, your speech is likely to improve as you get better. But there are situations when people need long-term speech therapy so they can communicate. If you have a speech impairment, your healthcare provider is your best resource for information.
There’s no way to prevent most speech impairments. You may be able to prevent some voice disorders by protecting your voice from overuse.
A speech impairment can affect your quality of life. Some suggestions for living with a speech impairment are:
Visit a healthcare provider as soon as you feel like something is affecting your ability to speak, hear or communicate with others. Visit a provider if you think your child might have difficulties with language or comprehension.
Advertisement
A sudden change in your ability to speak may be a symptom of a serious medical condition that needs immediate care. A stroke or head injury can affect speech. If you’re with someone who has the following symptoms, call 911 or your local emergency service number right away. To recognize the warning signs of a stroke, remember to think BE FAST:
Advertisement
A speech impairment happens when your mouth, jaw, tongue and vocal tract can’t work together to produce recognizable words. A language disorder happens when you have trouble understanding what others are saying. You may have trouble expressing your thoughts in ways that people understand.
Language changes. Over the years, people have called speech conditions by many names, including speech disorders, speech impediment and speech impairment. But these terms all have slightly different meanings.
The word “impediment” is obsolete in medicine. It’s from the 1600s and comes from the verb “to impede.” It refers to an illness or defect that hinders or gets in the way of (obstructs) functioning. Essentially, a speech impediment is something that blocks or hinders. Like a loose tooth or a new tongue piercing, it feels like something temporary or external that physically affects your ability to speak.
Now, people use terms like “speech disorder” and “speech impairment” instead. They both mean that something is going on that changes (disorder) or weakens (impairs) your ability to function or perform a task on a physical, psychological or structural (anatomical) level.
Speech is one way that we connect with the world around us. Having a speech impairment can make it hard to make that connection. It can be frustrating when you can’t communicate what you want people to know. Without treatment, a child with a speech impairment may have difficulty learning. Adults with speech impairments sometimes feel anxious and stressed about communicating using speech. Often, speech therapy can help. If you’re concerned about being able to communicate or think your child may have a speech impairment, talk to a healthcare provider. They’ll be glad to help.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Speech, language, comprehension and swallowing issues can make daily life harder. Cleveland Clinic speech therapists can help you overcome these problems.
