Scabies is caused by the Sarcoptes scarbiei mite. It causes an intense and itchy rash that can interrupt your sleep. Scabies spreads most often through direct contact with an infected person. Prescription medications can kill the mites and ease your symptoms.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
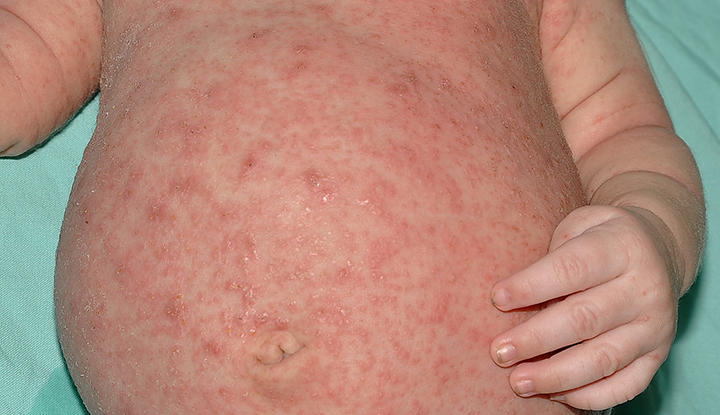
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/4567-scabies)
The Sarcoptes scabiei mite causes scabies. These little bugs make tunnels (burrow) under your skin to live, feed and lay eggs. Your skin reacts to the mite by developing an itchy rash. Scabies spreads easily from person to person, especially among people who live close together. If one family member has scabies, a healthcare provider should check and treat other family members and close contacts at the same time.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Scabies is a worldwide problem but happens most often in crowded, tropical areas, particularly in under-resourced countries. But it can affect people of all ages, races or economic status. It has nothing to do with how clean or hygienic you are. Healthcare providers treat scabies with medicated creams you apply to your skin or medication you take by mouth.
Yes, there are different forms in addition to the classic form. Other types include:
Scabies affects more than 400 million people each year worldwide. It’s generally more common in tropical countries that lack medical resources, but it can still occur anywhere. Scabies outbreaks in the U.S. and similar countries tend to occur in places where people share living space like nursing homes, dorms or correctional facilities.
Advertisement
Scabies causes an extremely itchy rash on your skin. It can take up to six weeks for this rash to develop if you’ve never had scabies, though. If you’ve had scabies before, you tend to get a rash within a few days.
The rash spreads slowly over weeks or months. In addition to the rash, signs and symptoms of scabies include:
Children with scabies may have itching all over their bodies and might be cranky or tired from lack of sleep due to itching at night.
The mites live in the folds and cracks of your skin. Common mite sites include:
The scabies mite is very small, about the size of the tip of a needle, and very difficult to see. It’s white to creamy white. It has eight legs and a round body, which you can see if the mite is under a microscope.
The skin rash can appear in different colors depending on your skin tone. For example, it can look red, brown or gray. The rash can look like hives, insect bites or pimples. It can even appear in a line across your skin.
Scabies is a mite infestation. These tiny mites burrow under your skin to live, eat, poop and lay eggs. Your skin reacts to this by swelling and itching, much like your skin reacts to an allergy.
Scabies mites spread from person to person. Direct contact with a person’s skin is the easiest way to spread scabies. Less commonly, you can also get it through sharing bedding, clothes or towels with someone who has the disease.
No. The mites that affect your pet can’t live on humans.
Anyone can get scabies. It’s not a disease you get from poor hygiene. Some people are more likely to get scabies, including:
Scabies can cause complications like:
Make an appointment with your healthcare provider if you think you (or your child) have scabies. Your provider can often diagnose scabies by just looking at your skin.
Advertisement
Your healthcare provider may also apply mineral oil to the rash and use a scalpel to get a small sample of skin (scraping). They examine the sample under a microscope to look for mites and mite eggs.
Scabies treatment may involve medication you apply directly to your skin or medication you swallow. The goal of treatment is to kill the mites, although you can still itch for weeks afterward. Medication can’t kill mite eggs, so you may need to repeat treatment if your symptoms continue.
Recent sexual partners and anyone who lives with you also need treatment.
Healthcare providers may prescribe a cream, lotion or ointment to treat scabies. You put the medication on your whole body from your neck downward, including your hands, palms and feet. Children with scabies may need medication on their faces and scalps.
Follow the instructions on the package or from your healthcare provider. Most creams need to stay on your skin for eight to 14 hours. In most cases, you’ll apply the medication at bedtime and wash it off in the morning.
Your provider may prescribe the following topical medications:
Medications you swallow by mouth are another option. Your provider may recommend oral medication if you need a stronger medication or if you can’t use topical medications.
Advertisement
Ivermectin is the most common medication to treat scabies. This is an antiparasitic pill given in a single dose, followed by a second dose one to two weeks later. Children less than 35 pounds (15 kilograms) and women who are pregnant or nursing can’t take this medication.
Other medications your provider may recommend include:
The red bumps on your skin should go away within four weeks after treatment.
One treatment with a topical cream or pill kills the mites that cause scabies. You may still have a rash or itch for up to two weeks, but the mites usually die after one dose of medication.
The itching may take two to four weeks to go away (even when all the mites are dead).
No, scabies won’t go away on its own. Only prescription medication can treat it. If you don’t treat it, you’ll probably continue to spread the disease to other people. In addition, the constant itching will probably lead to constant scratching and a skin infection.
Scabies is treatable but can be hard to get rid of completely. Certain forms of scabies are harder to treat, such as the crusted form. In addition, you might need more than one round of treatment to make sure all the mites are gone.
Advertisement
While scabies can be frustrating and uncomfortable for several weeks, your healthcare provider can prescribe medication to get rid of the mites and help ease your symptoms. It may take up to two months for your skin to heal.
Talk to your healthcare provider if you don’t see your symptoms improve with medication or if you still have a rash after four weeks. You may need repeat treatment to get rid of any remaining mites.
Be sure to wash your bedding, clothing and towels and clean the floors in your home. While mites can’t live on these surfaces for more than a few days, you should still eliminate the mites that lurk outside of your body.
In most cases, your child can return to school the day after treatment begins. If you’re an adult, you can go back to work after you begin treatment. Check with your healthcare provider to be sure.
Yes. You can get scabies any time you come into close contact with an infected person.
You can prevent spreading scabies by:
Place unwashable items like stuffed animals, large pillows and toys in large garbage bags. Place the bags in a garage or basement for about seven days. Mites on these surfaces will die within a few days without human skin. You can then remove the items from the bags and wash them off by hand.
There’s no vaccine to prevent scabies. The only way to prevent getting scabies is to avoid people or places with known scabies outbreaks. The disease spreads easily among people who live in the same household or share a room.
Call your healthcare provider if you have scabies and you:
If you find out you have scabies, it’s normal to have questions. Some questions to ask your provider are:
No, you can’t feel the mites crawling on you because they’re tiny and crawl slowly. The only thing you can feel is the itchiness or inflammation they cause to your skin.
Mites may temporarily live on or in a mattress, but they need human skin to survive. Mites can appear on virtually anything — furniture, clothes or surfaces — but they’ll die after a few days.
Dirty sheets don’t cause scabies because the disease isn’t related to hygiene or cleanliness. But scabies can spread from person to person through bedsheets.
If you have a rash and it’s so itchy you can’t sleep, make sure you contact your healthcare provider. You may have scabies, which is an infectious disease caused by tiny mites. You and other people close to you should receive treatment right away for scabies. You’ll want to contact your healthcare provider if you have any kind of skin rash that doesn’t go away and that causes problems for you. Scabies, like many other types of red and itchy rashes, is treatable with medication.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Need care fast? Cleveland Clinic’s Express Care and Urgent Care locations treat everything from sprains to sinus infections — no appointment needed.
