The interstitium are small fluid-filled spaces that cushion organs, move nutrients and help clear waste. These spaces are supported by a framework of tissue that keeps everything connected and balanced. The interstitium plays a key role in keeping your organs healthy and your body running smoothly.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
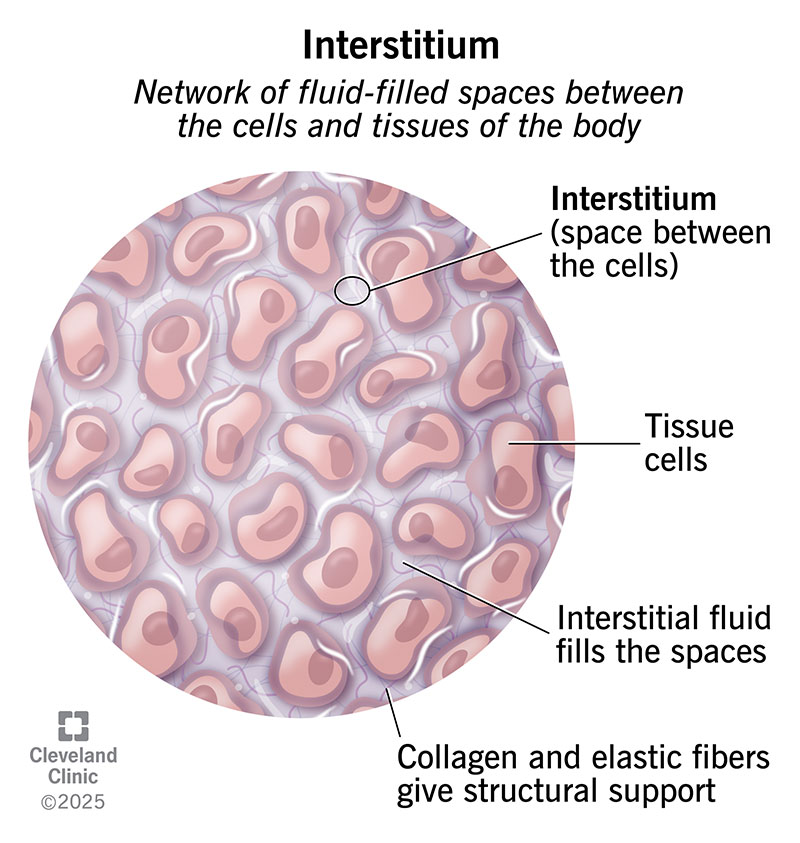
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/interstitium)
The interstitium are fluid-filled space between the cells and tissues in your body. These spaces help support, cushion and connect your cells. Intersitium also plays a role in moving nutrients, fluids and waste between your cells. It keeps your cells and tissues healthy so they can perform important tasks.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Even though you can’t see it (and maybe have never heard of it), it’s a major player in keeping your body balanced and running smoothly. Up until 2018, scientists didn’t know how complex and vast the interstitium was. They now believe it’s an important part in helping your body function.
The interstitium has a few jobs:
The interstitium is everywhere. It’s part of all of your organs, muscles, tissues, nerves and blood vessels.
It’s a large network of small spaces, fluid and supportive material between your cells, tissues and organs. It’s made up of:
Advertisement
As the interstitium is everywhere, problems with it can show up in almost all areas of your body. Some of the medical conditions that affect the interstitium are:
We’re always learning more about our bodies. And the interstitium is one of those newer discoveries. This may be the first you’ve ever heard of it. But it’s a complex support network for your cells and tissues. Without it, your cells couldn’t work. Most of the time, your interstitium works quietly in the background. But if you notice swelling, slow-healing wounds or general inflammation, it could be a sign that the interstitium isn’t working as it should.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s primary care providers offer lifelong medical care. From sinus infections and high blood pressure to preventive screening, we’re here for you.
