An EEG (electroencephalogram) is a test that tracks your brain’s electrical signals. It checks for epilepsy or other brain conditions. It’s painless, safe and can be done while you’re awake or asleep. Your provider will use the results to help guide a diagnosis and treatment.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
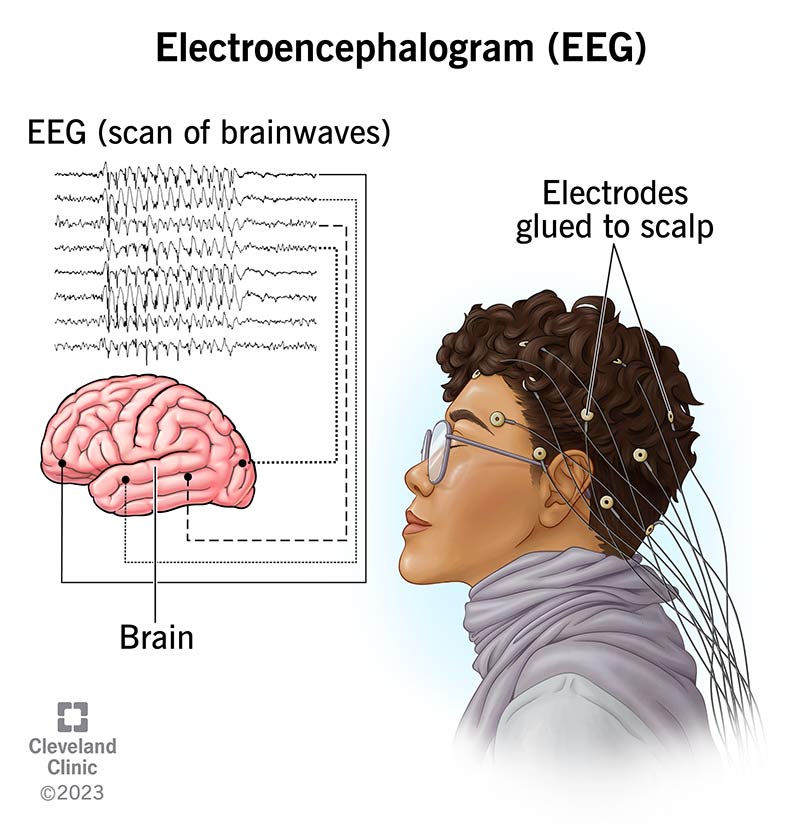
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/9656-electroencephalogram-eeg)
An EEG (electroencephalogram) measures the electrical activity in your brain. Healthcare providers often use this test to diagnose conditions like epilepsy.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Providers may use the term EEG to describe the test itself and what it shows.
During this test, a technician places small, metal disks (electrodes) on your scalp. The electrodes connect to a machine that records the electrical signals your brain cells (neurons) use to communicate. Tracking these signals shows how well different parts of your brain are working.
Healthcare providers often order this test if you have seizures or if they suspect epilepsy. They may also recommend one if you have symptoms like:
EEGs can also monitor brain activity in certain conditions, including:
Providers order different types of EEGs depending on the medical issue. These include:
Advertisement
This test measures the electrical signals (impulses) that pass between your brain cells. Electrodes on your scalp pick up these signals through small wires. The process works like this:
There are different types of EEGs. Your healthcare provider will explain which test you need and why. They’ll also tell you what to expect, how long it’ll take and if you’ll need a ride home afterward. No matter the type you need, you should:
Most EEGs need little preparation, and your provider will give you clear instructions.
During a routine EEG:
A routine EEG may take 20 to 30 minutes to complete. The time depends on the type. But your provider will tell you in advance so you know what to expect.
This test rarely causes side effects. Some people feel dizzy while taking deep breaths. If you have certain types of epilepsy, deep breathing (hyperventilation) or flashing lights (photic stimulation) may trigger a seizure. This is uncommon. Your technician will know how to help if anything happens.
You may also notice minor and temporary hair loss or skin irritation where the electrodes were placed.
Your technician will remove the electrodes and clean your scalp. Unless your provider gives you other instructions, you can go home and return to your normal activities.
Your hair or skin may feel sticky from the glue or paste used for the electrodes. You may want to wash your hair when you get home.
You’ll have a follow-up appointment with your doctor after the test. The timing can vary, but they’ll see you as soon as possible. During the visit, they’ll review your brain wave patterns and explain the next steps.
That depends on your situation. Your healthcare provider may refer you to a specialist, like a neurologist, who can diagnose, treat or manage the condition.
Advertisement
An EEG might sound a little intimidating at first — wires, electrodes, machines tracking brain waves. But the test itself is painless. And it gives your care team important clues about what’s going on in your brain.
Whether you’re dealing with seizures, memory changes or just trying to get answers, an EEG helps piece together the full picture.
Most people can return to their usual routine right after the test. And if something unusual shows up, your provider will walk you through the next steps. Your brain is powerful and complex. This test is one way to help understand it a little better.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
If you have a neurological condition, you want expert advice. At Cleveland Clinic, we’ll work to create a treatment plan that’s right for you.
