A birth control implant is a small, thin rod-like device you wear under the skin in your arm to prevent pregnancy. The implant releases the hormone progestin into your bloodstream. It’s effective for five years.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
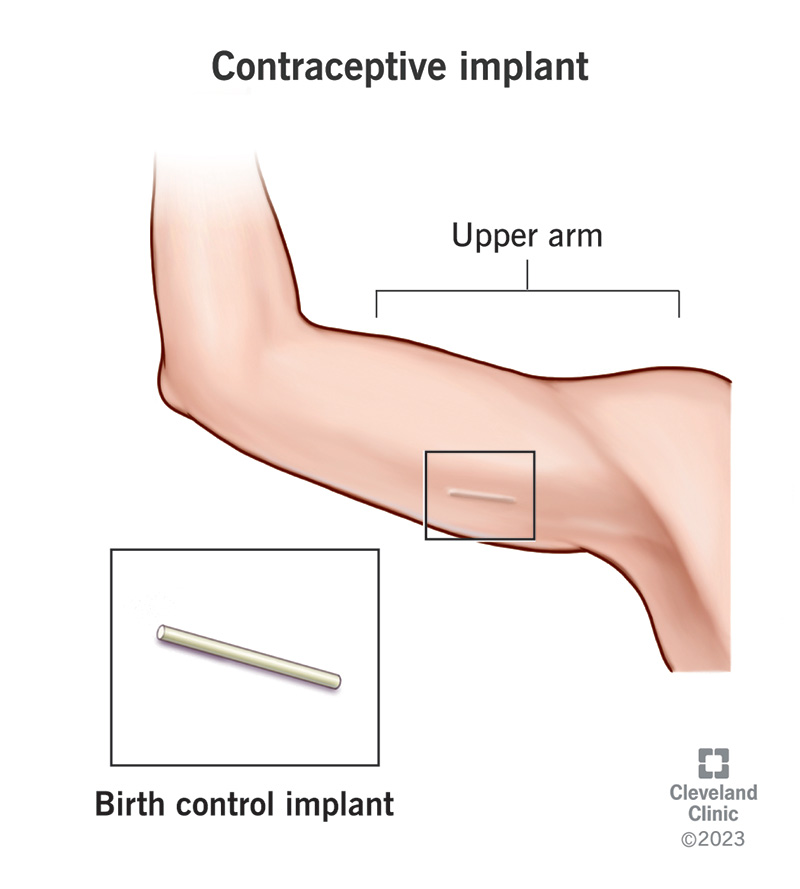
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/24564-contraceptive-implant)
A contraceptive implant (birth control implant) is a small, flexible rod-like device that your provider inserts under your skin in your inner, upper arm. It releases a steady dose of the hormone progestin into your bloodstream to prevent pregnancy for five years. Nexplanon® is the brand name of the birth control implant. A healthcare provider must insert and remove a birth control implant. Birth control implants are one of the most effective forms of birth control available.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
The implant is about 1.6 inches (in) long (4 centimeters, or cm) and approximately one-eighth inch in diameter. It’s flexible (you can bend it) and about the size of a matchstick.
The implant releases a slow, steady dose of progestin (a hormone) into your body. Progestin prevents your ovary from releasing an egg (ovulation). It also thickens the mucus in your cervix, which makes it hard for sperm to reach an egg (in the rare chance ovulation happens). Progestin also thins your uterine lining, making it difficult for a fertilized egg to implant.
The birth control implant is effective for up to five years.
The birth control implant is one of the most effective options available (the other being an IUD). Studies show it’s more than 99% effective in preventing pregnancy.
Your healthcare provider inserts the birth control implant in their office using the following steps:
Advertisement
A healthcare provider must remove your birth control implant. The contraceptive implant is currently approved for five years. It can be removed at any time after placement based on your preference. Discuss the timing of removal with your healthcare provider.
Removing an implant involves your provider making a small incision in your skin and removing the implant. Your provider will still numb your arm before the procedure so you don’t feel pain. To remove an implant:
You should never attempt to remove your implant. Only trained providers should insert and remove birth control implants. Once your implant’s out, you’re not protected against pregnancy. Use an alternate form of birth control if you don’t want to become pregnant.
It may feel uncomfortable for a moment, but it shouldn’t hurt. Some people say the numbing medication feels like a pinch. You may feel soreness or tenderness around the implant for a few days.
Your healthcare provider can put the implant in at any point in your menstrual cycle (as long as you’re not pregnant). If your provider inserts it during the first five days of your cycle, it protects you against pregnancy immediately. If it’s after five days into your cycle, you should use a backup contraception (like a condom) for seven days.
The birth control implant isn’t known to have many side effects. Most side effects subside within a few months. Some of the potential side effects are:
Let your provider know if you have side effects that last longer than a few months. There may be some ways to treat side effects prior to the removal of the device. But your provider can remove your implant at any time and you can try another type of birth control.
It’s important to weigh all your options for birth control before making a decision. There are advantages and disadvantages to the birth control implant. Talk to your healthcare provider about the risks and benefits of the implant to decide if it’s right for you.
Advertisement
The birth control implant is a safe and effective way to prevent pregnancy. However, it may not be for everyone. Tell your provider about your medical history so they can help you decide if a contraceptive implant is right for you. It may not be for you if:
Some people stop getting their period with the birth control implant. It’s not harmful to your health not to get a period. However, some people don’t like having irregular or absent periods. Talk to your healthcare provider about what you can expect.
No. Research has shown that weight gain isn’t a direct side effect of the birth control implant. However, some people still report feeling bloated or gaining weight while using the implant.
The birth control implant is more effective than the pill at preventing pregnancy. This is mainly because you don’t have to remember to take the implant like you do with a pill. However, the best birth control is one you’ll use correctly. Some people prefer a daily birth control pill, but others like the convenience of an implant. There are other factors that can affect which birth control method your provider recommends. It’s important to discuss your options with your provider.
Advertisement
It’s rare for the implant to break or bend in your arm. If you’ve been in an accident or experienced trauma to your arm, there’s a small chance it shifts the implant or damages it. If you believe this is the case, please contact your provider as soon as possible.
It’s rare for the implant to get lost in your arm. Once the implant’s in, it’s common for your skin to react by thickening the tissue around the implant in an attempt to heal the area. This is also why it’s sometimes harder to remove the implant.
Only you and your provider can decide what birth control method is best for you. It may come down to your preference or your health history. An IUD and an implant are similar. Some of the similarities include:
It’s possible to get pregnant as soon as your provider removes your implant. This means you may ovulate within a few days. If you’ve had intercourse in the week prior to implant removal, it’s possible that sperm could still be in your body. This means if ovulation occurs, sperm could fertilize an egg.
Advertisement
It takes about 14 days for a pregnancy test to detect pregnancy after ovulation. Once your implant is out, you could take a pregnancy test around this time to confirm pregnancy hasn’t occurred. If you don’t want to get pregnant, consider using an alternate form of birth control as soon as your implant is out.
If you have a birth control implant, you should contact your provider if you have:
A birth control (contraceptive) implant is a highly effective form of birth control that a provider places under your skin. It releases progestin into your bloodstream to prevent pregnancy for up to five years. Some people love the implant because it’s low-maintenance and convenient. However, the implant isn’t for everyone. Discuss the risks and benefits of the implant with your provider. Together, you can decide if this is the right birth control method for you.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Your birth control needs to work for you. At Cleveland Clinic, we help you find the right birth control option to fit your goals and lifestyle.
