Ranulas are cysts on the floor of your mouth. The cysts are filled with saliva (spit) that leaks from your salivary gland. The cysts don’t hurt but can grow large enough to cause difficulty breathing or swallowing. Ranulas happen when something blocks or damages your salivary gland. Ranulas may heal on their own, but some require treatment.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
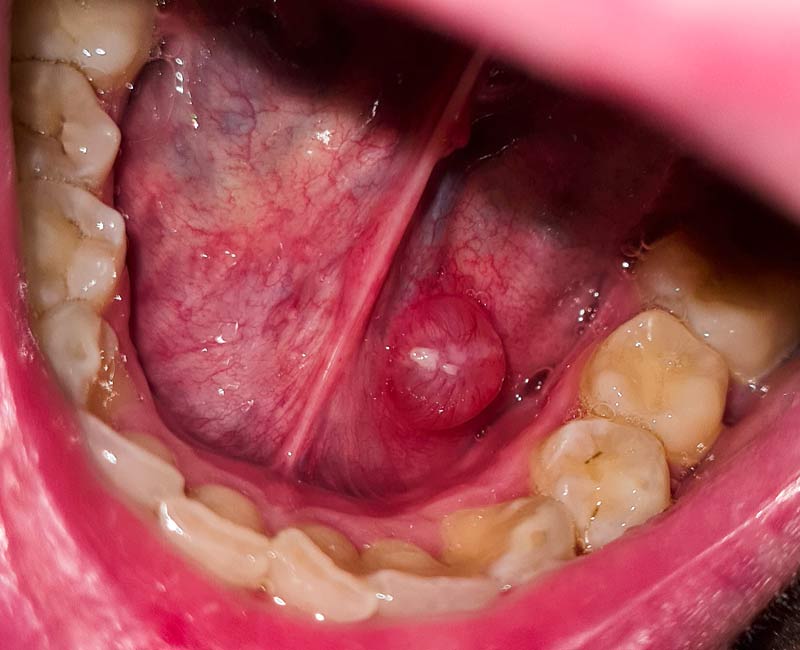
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/Images/org/health/articles/ranula-mouth-cyst)
A ranula is a fluid-filled cyst on the floor of your mouth, under your tongue. It forms when saliva (spit) from a salivary gland leaks into tissue around the gland. Eventually, saliva builds up and creates a squishy lump on the floor of your mouth or swelling in your neck. You may get a ranula (pronounced “ra-NOO-luh”) if something blocks or damages the gland so saliva can’t flow into your mouth.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Ranulas aren’t cancer or a serious medical issue. Some go away without treatment. But the lump under your tongue may change the way you talk or eat. Some can grow so large that they make it hard to breathe or swallow. In that case, you may need treatment to drain fluid from the ranula or to remove it.
There are two types:
Symptoms may include:
Ranulas usually aren’t painful. But the sensation of a lump under your tongue or swelling in your neck may make you uncomfortable. A large ranula can push your tongue out of place. That can affect how you talk or eat. For example, you may talk with a lisp or eat very slowly.
This condition may develop when something blocks or damages your salivary gland. But sometimes, there’s no clear cause.
People of any age and sex can get ranulas. But they’re more common in children and adults ages 20 to 40.
Advertisement
A large ranula can affect your breathing if it presses on your windpipe. It can make it hard for you to swallow.
A healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms. They’ll look under your tongue and check your neck for swelling. They may request imaging tests, including:
Your treatment will depend on your symptoms and the size of the ranula. Some go away on their own. But you may need treatment if the ranula makes it hard to breathe or swallow. Procedures include:
Recovery depends on what treatment you had. For example, a cut to drain a ranula should only take a couple of days to heal. It may take one to two weeks to recover from surgery to remove your salivary gland and the ranula.
Contact a healthcare provider if you notice a lump under your tongue or swelling in your neck — even if it comes and goes.
If you had surgery to remove a ranula and salivary gland, you should contact your provider if you experience:
This isn’t a serious medical condition. Some go away without treatment. In some cases, treatment to drain a ranula takes care of your symptoms. But a ranula may come back. Surgery is the only permanent solution.
No. Ranulas happen when something blocks or damages your salivary gland. They aren’t caused by STIs.
The term “mucocele” refers to any type of mucus-filled cyst in the inside of your mouth. A ranula is a specific type of mucocele.
Ranulas — fluid-filled cysts under your tongue — aren’t serious medical issues. But you may feel self-conscious if the lump changes the way you talk or eat. Larger ranulas can affect your breathing or make it hard to swallow.
Talk to a healthcare provider if you have a lump under your tongue that doesn’t go away or gets bigger. They’ll check the lump and recommend the treatment that’s right for you.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
If you have conditions affecting your ears, nose and throat, you want experts you can trust. Cleveland Clinic’s otolaryngology specialists can help.
