Blount’s disease is a condition that affects how the shin bone (tibia) grows in toddlers and adolescents. Blount’s disease causes a bow or bend in the leg below the knee. The condition is most common among early walkers or children who gain weight quickly. Treatment corrects the bowed leg with a brace or surgery.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
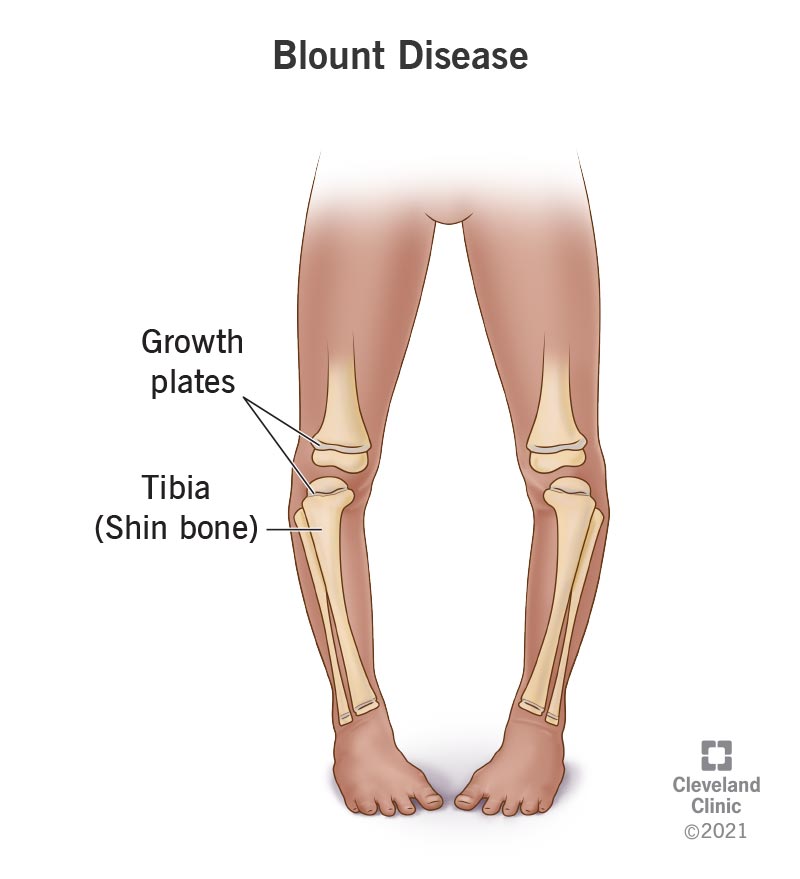
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/22424-blounts-disease)
Blount’s disease, also known as tibia vara, is a growth disorder that affects the growth plates of the shin bone (tibia). Blount’s disease causes a child’s lower leg to turn inward and bend to resemble the curve in the letter C.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Infants and toddlers naturally have bowed legs (a curve to their legs), but the bend in their legs straightens out when the child begins to walk. Children diagnosed with Blount’s disease have a distinct curve in their legs that doesn’t resolve as the child ages and gets worse as their bones grow.
Although both Blount’s disease and bowed legs look similar, there are differences between the two conditions. Children have a natural curve to their legs (bow) during infancy and early childhood. When children start to walk, that bow straightens out over the first two years of life. Children diagnosed with Blount’s disease have a severe inward bend in their lower legs (below the knee). The bow shape in Blount’s disease is very distinct and doesn’t adjust itself as the child grows, whereas children with bowlegs naturally grow out of the condition.
Blount’s disease affects infants older than one year. The condition becomes noticeable between one and three years of age (early-onset). Blount’s disease can develop later during adolescence and among adults (late-onset). The condition is common among people who are overweight, people who gain weight quickly or children who start walking early (before 12 months).
Advertisement
Blount’s disease is rare and affects less than 1% of the population.
Blount’s disease affects how your child’s shin bone grows. This could cause their leg to bend inward, so their toes face in instead of straight and their leg forms a curve. If left untreated, this condition could get worse and the bend could prevent your child from walking or participating in physical activities where they use their legs. It can also cause nerve damage in your child’s legs and arthritis, which can be painful.
The biggest symptom of Blount’s disease is a bend of the leg below the knee (bowing). Symptoms of Blount’s disease include:
Bowing doesn’t cause pain in toddlers but adolescents may feel knee pain that gets worse with physical activity.Severe symptoms of Blount’s disease include:
The exact cause of Blount’s disease is unknown. Studies show that children who walk before 12 months and adolescents who gain weight rapidly are more at risk of acquiring Blount’s disease. Other studies suggest that the condition could be genetic.
In some cases, Blount’s disease is hereditary (inherited from your parents) and runs in families. Growth plates (area at the end of bones that is responsible for new bone growth) of the inner part of the shin bone (tibia) don’t develop normally for people diagnosed with Blount’s disease. The cause of underdeveloped growth plates of the tibia could link to a gene that you acquire from your parents during conception.
Your healthcare provider will diagnose Blount’s disease after performing a physical examination as well as ordering X-rays of your child’s legs (ankle to hip). X-rays help your provider see how your child’s bones are growing and can help them identify what is making your child’s leg curve inward.
Diagnosis happens after two years of age because natural bows in children’s legs straighten out during this time. If there is still a bow in your child’s legs after two years, your healthcare provider will suspect Blount’s disease and offer imaging tests to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment varies for each person diagnosed with Blount’s disease and could differ based on age and severity of the bend. Treatment could include:
Advertisement
After surgery to treat Blount’s disease, it’s important to monitor your child’s surgical site for infection and make sure your child doesn’t put weight on the affected leg(s) for six to eight weeks. Putting too much stress on the surgical site could cause the bone to shift and not heal correctly.
The prognosis for people diagnosed with Blount’s disease varies based on the age and severity of their diagnosis. Children younger than four years old who receive treatment have a good outlook. If Blount’s disease isn’t diagnosed and treated early, the bow could become worse, which puts your child at risk of severe joint damage and difficulty walking.
There is a chance that the bow could return after treatment in both children and adolescents, but the risk is low if the condition receives treatment early in the diagnosis.
Blount’s disease can last a lifetime if not treated and can get worse as your child grows. Depending on the severity of your child’s diagnosis and after treatment, the bow in their leg will improve either after they heal from surgery or after a year of wearing a brace. There is a risk that the bow could return after treatment, so make regular appointments with your child’s healthcare provider to monitor the effectiveness of their treatment plan.
Advertisement
There is no known way to prevent Blount’s disease, but you can take steps to help your child’s bones grow healthy and strong by making sure they:
Check with your child’s healthcare provider that it’s safe to start taking any vitamins or supplements.
You should visit your healthcare provider if you notice your child’s bowed legs don’t correct themselves when your child starts walking or by the time they turn two years old. You should also visit your healthcare provider if your child experiences pain associated with the bow in their leg or they are unable to walk or put pressure on their leg(s).
Bowed legs naturally occur in infants and go away when your child begins walking or by the time they turn two years old. If you notice your child’s legs don't straighten out or their bow becomes more defined as they age, visit your healthcare provider for an evaluation. Early diagnosis and treatment most effectively stop the bow from becoming worse and prevent complications like arthritis and nerve damage from arising.
Advertisement
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic's health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability, and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic's health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability, and up-to-date clinical standards.