Your trapezius muscles are two big muscles on either side of your upper back. They help you move your head, neck and upper back, and maintain and adjust your posture. Overuse, injuries and nerve damage are the most common causes of trapezius muscle pain.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
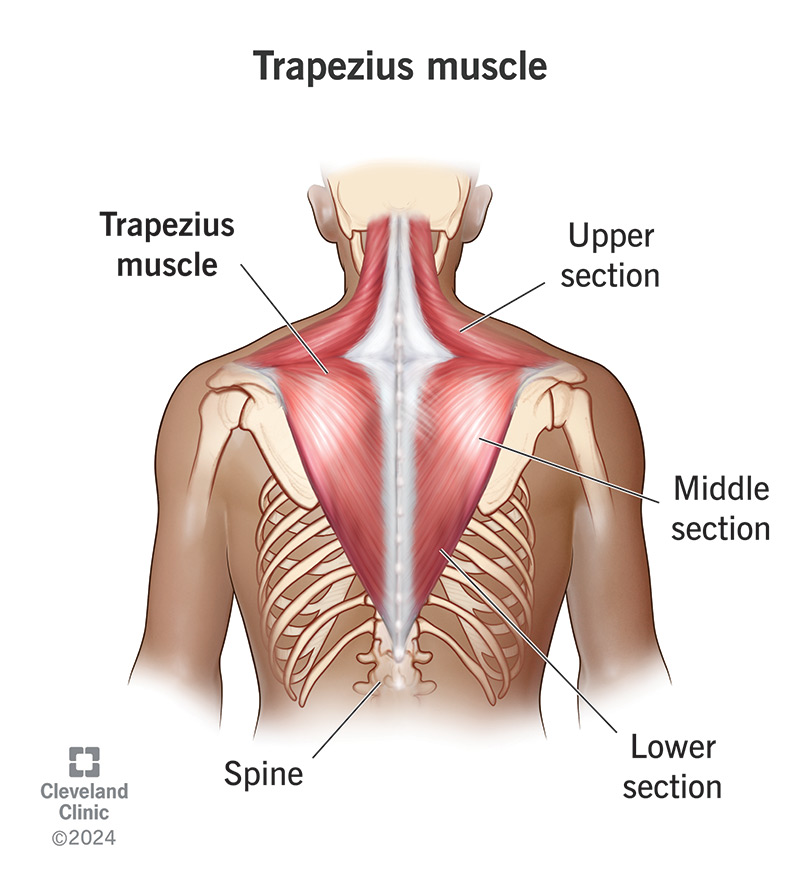
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/trapezius-muscle)
The trapezius is a large muscle in your back. People commonly refer to trapezius muscles as traps or trap muscles.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Like the rest of your back muscles, your traps are skeletal (superficial) muscles and are part of your musculoskeletal system.
Your trapezius muscles are big, and you use them a lot throughout your day. It’s less common to injure them than other muscles, but it’s possible. Visit a healthcare provider if you’re experiencing pain in your back, neck or the back of your head that lasts for more than a week.
Like the rest of your back muscles, your trapezius muscles support your body and help you move. Your traps help you do many motions, including:
You use your trapezius muscles almost constantly throughout your day. But you may never purposefully think about them. Lots of these motions and movements are small tweaks to how you’re holding your head, neck, back and shoulders. You might only focus on your traps when you’re working out, or after reading the previous sentences about how they help you change your posture while you wiggle in your seat.
Advertisement
You have one trapezius muscle on either side of your upper back. They start at the base of your neck and extend across your shoulders and down to the middle of your back.
Trapezius muscles get their name from their shape. If you look at them together, they form a trapezoid (a shape with four sides, two of which are parallel). They’re shaped a bit like a kite.
Each trapezius muscle has three sections:
Your traps connect to your skull, spine, ribs and bones in your shoulders. The upper section connects to your skull and neck (cervical spine).
The middle and lower sections attach to bones in your thoracic spine. They’re also connected to the back (lateral) sides of your shoulder blade (scapula) and collarbone (clavicle).
Cranial nerve XI (the spinal accessory nerve) lets your trapezius muscles move. They get their sense of feeling from the C3 and C4 cervical nerves in your neck.
Your trapezius muscles can feel a few types of pain if they’re injured or irritated, including:
Other symptoms of trapezius injuries or issues can include:
Some of the most common issues and injuries that can cause trap muscle pain include:
Advertisement
To keep your muscles strong, you should focus on staying healthy overall. To avoid problems with your trapezius, you should:
It might sound like your trapezius muscles get their name from a high-flying circus act, but these big muscles in your upper back help keep you grounded. They hold you in place and maintain your posture. They also support and help you move your head, neck and back.
Everyone experiences back pain from time to time. See a healthcare provider if you’re feeling pain in your upper back, neck or head for more than a week. They’ll help you understand what’s causing it and how you can manage it.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
From sudden injuries to chronic conditions, Cleveland Clinic’s orthopaedic providers can guide you through testing, treatment and beyond.
