A tooth abscess is a pocket of pus (infection). It damages oral tissues and can spread to other areas of your body, causing serious health issues in some cases. An abscessed tooth won’t heal on its own and requires treatment from a dental healthcare provider.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
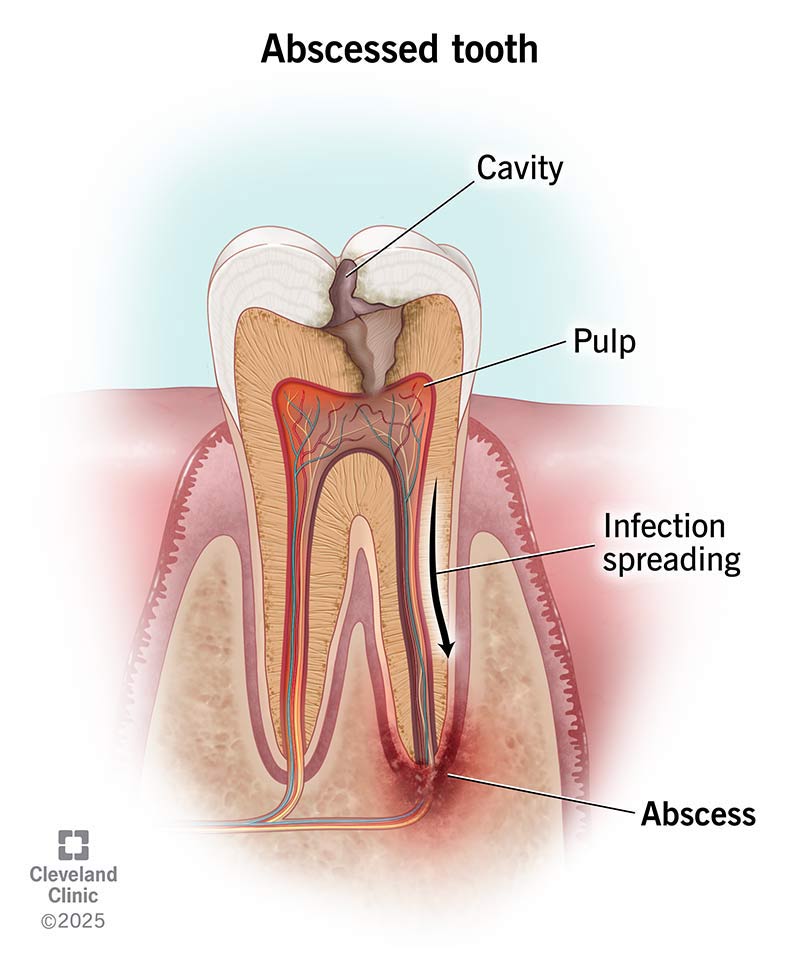
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/abscessed-tooth)
A tooth abscess is a pocket of pus from a bacterial infection in your gums. An abscess usually looks like a red, swollen bump, boil or pimple. It affects the involved tooth, but the infection can also spread to surrounding bone and neighboring teeth. Abscesses can occur in various places around a tooth for different reasons.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Three types of tooth infections can cause abscesses:
Left untreated, a tooth abscess can spread to your jawbone, the soft tissues of your face and neck, and beyond. In extremely rare cases, the infection can travel to your heart (endocarditis) and brain (bacterial meningitis).
This is why it’s so important to see a dentist as soon as possible if you have symptoms of a tooth abscess.
A tooth abscess can cause severe tooth pain. It may feel shooting, throbbing or like it’s radiating to your ear, jaw or neck. It may hurt all the time or only when you’re chewing.
Advertisement
Other symptoms include:
Anything that creates an opening for bacteria to get into a tooth or surrounding tissues can lead to an abscess, such as:
You’re more likely to develop an abscessed tooth if you:
In addition to examining the tooth and surrounding tissue for signs of infection, your dentist may:
The goals of treatment are to eliminate the infection and prevent complications. Treatment options include:
Advertisement
A tooth abscess should clear up after treatment. Temporary sensitivity is common, and it may take a few days to feel completely back to normal.
As every case is unique, healing times can vary. Ask your dentist what to expect after your tooth abscess treatment.
If you develop mouth pain, a toothache or a red, swollen bump on your gums, schedule an appointment with a dentist right away. The sooner you get treatment, the less likely it is that the infection will spread beyond your tooth.
Head to your nearest emergency room if you have a tooth abscess accompanied by:
A tooth abscess won’t go away on its own. Pain may stop if an infection causes the pulp inside your tooth to die. The pain stops because the nerves in the pulp aren’t working anymore, so you may not be able to feel it. But the bacteria will continue to spread and destroy surrounding tissue.
If you have tooth abscess symptoms, seek care even if you no longer have pain.
Left untreated, a tooth abscess will eventually spread to the surrounding tissues and beyond, wreaking havoc on your oral and overall health. It can take days, weeks or months for the infection to spread — and it’s impossible to know exactly how long that will take. Because tooth abscesses don’t go away on their own, it’s critical that you see a dentist as soon as possible.
Advertisement
Tooth pain is a sign that you should see your dentist. While you wait for your appointment, warm saltwater rinses and over-the-counter pain relievers (like acetaminophen, naproxen or ibuprofen) can ease discomfort.
But it’s important to remember that there isn’t a tooth abscess home remedy that can permanently solve the issue.
You can reduce your risk of developing a tooth abscess by seeing your dentist routinely and getting regular dental check-ups and cleanings. It’s also important to see your dentist if a tooth becomes loose or chipped.
Remember that proper oral hygiene is essential for dental health. At home, brush your teeth twice a day and floss once a day.
All tooth abscesses are also infections. But not all tooth infections lead to an abscess (pocket of pus).
If it helps, think of an abscessed tooth as a sign of a severe tooth infection. The pocket of pus contains dead tissue and dead or dying white blood cells — your body’s infection fighters. Pus is like the rubble that remains after your immune system does battle with a major infection.
But the pus contains the bacteria that are still around and ready to do even more damage. It can spread without treatment.
This is why you want to get treatment for dental infections so they don’t become abscessed.
Advertisement
It’s important to take a tooth abscess seriously. Without treatment, it can damage oral tissues and even spread to other areas of your body. But getting treatment fast can prevent this from happening. You may be able to save the affected tooth. If you have symptoms of an abscessed tooth, don’t put off seeking care. It’s important to see a dentist ASAP.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic's health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability, and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic's health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability, and up-to-date clinical standards.
Dentistry plays an important role in oral health. Cleveland Clinic’s experts can design a personalized plan that will keep you smiling for the long haul.
