Overview
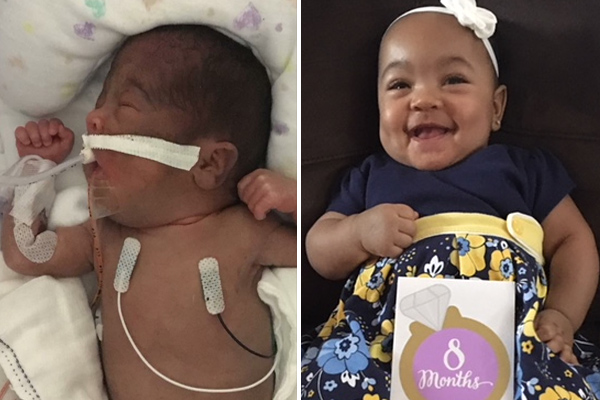
Your baby’s journey doesn’t always end when they leave the NICU. Our team of neonatologists, nurse practitioners, and occupational therapists provide specialized monitoring to ensure every child reaches their full potential. Studies show that early, expert support gives babies the strongest foundation for a healthy future.
We identify developmental delays early and connect your family with the right tools for long-term growth, specifically focusing on:
- Feeding challenges and nutrition.
- Movement and muscle tone concerns.
- Developmental progress to ensure milestones are met on time.
Is the NICU Follow-up Clinic right for your baby?
We see infants referred by pediatricians or specialists, but parents can also schedule an evaluation directly if they have concerns about their child's development.
Your baby may qualify if they:
- Were born early or small: Born before 32 weeks or weighing less than 3 lbs. 5 oz. (1500 grams).
- Need extra equipment at home: Such as oxygen or a feeding tube (NG tube).
- Experienced birth complications: Including HIE (brain injury from oxygen loss) or NAS (withdrawal from prenatal exposure).
- Have complex conditions: Including major surgical procedures or chromosomal and congenital conditions.
Timing of Follow-up Visits
Some developmental challenges may not be clear right after birth. Because of this, our team typically schedules follow-up visits when babies reach these ages:
- 4 months corrected age*
- 8-12 months corrected age*
- 18-24 months corrected age*
To offer continued support and check on how both the baby and parents are adjusting, visits can start as early as 2 to 4 weeks after discharge. This dedicated support may continue up to age three, based on the child's needs.
*Corrected age is calculated by counting the number of months from the baby's original due date, not their actual date of birth.
What to Expect
Although each baby’s needs are different, at each appointment we review the complete medical history of the child including NICU stay and post NICU events. Current medications, therapies and treatments are reviewed. A complete Physical Examination is also performed. We then discuss parent and provider concerns and jointly come up with a plan that is best for the parent and the child.
Even though each baby’s development is different, we conduct formal developmental assessments at specific times to give parents information about an infant’s cognition, language skills and motor development.
Between 8 and 12 months corrected age and again between 18 and 24 months corrected age, a pediatric occupational or physical therapist will assess your child using a standardized test, the Bayley Scales of Infant Development, Third Edition (BSID-III).
This assessment helps compare your child’s development with normally developing children of the same corrected age (if born preterm); keeping in mind there is a wide range of normal development. The BSID-III can determine strengths or indicate specific therapeutic areas to focus on, such as can be accomplished in physical, occupational and/or speech therapy. It can also help determine if further assessment is needed.
At 18 months corrected age, we use the Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers-Revised (M-CHAT-R) to identify children who may benefit from a more thorough evaluation for autism.
We may also schedule earlier or additional visits if you, another provider or we have specific concerns.
At times, we can arrange on-site visits from social services, nutrition or therapy services, and/or consultation with other physicians who may assist with your child’s care.
What BSID-III Testing Involves
The BSID-III is a standardized test that examines cognition, language, motor, social-emotional, adaptive and behavioral skills in children ages 1-42 months. The examiner uses various toys as well as observation during BSID-III testing to look at these areas:
Cognition: The child’s ability to recognize certain objects or toys, to play with toys and to engage in pretend play is assessed.
Language skills: The child’s receptive (understanding) and expressive (talking) abilities are evaluated. Receptive abilities include responding to the sound of a person’s voice, distinguishing between sounds, localizing sound, and understanding and responding appropriately to words and requests. Expressive abilities include talking, communicating wants or needs through words or gestures, naming pictures of objects and actions, answering questions, and using multiple word sentences.
Motor skills: The child’s muscle coordination, balance, and fine and gross motor skills are assessed. Fine motor skills are the coordination of the small muscles, usually involving the hands and fingers. Gross motor skills are involved in the movement and coordination of the arms, legs and trunk.
Other areas: Based on a parent’s or primary caregiver’s responses to an optional questionnaire, we may evaluate the child’s social-emotional and adaptive skills as well. The examiner and parent/caregiver may complete behavioral evaluation based on behavior during the test and at home.
Babies may benefit from early physical, occupational speech and or feeding therapy based on developmental test results.
Scoring: The testing looks at how a child performs compared to other children of the same corrected (not chronological age if preterm). Scores, percentile ranks and age equivalents are determined.
Sharing results: We discuss each child’s strengths in detail with family members and offer recommendations aimed at reinforcing and/or improving development. Further testing and/or therapy may be prescribed.
Test results (but not the child’s name) may be shared with NICU staff to help us study how to improve the quality of care. No information with patient identifiers is used for research purposes without a signed informed consent form from the parent or guardian.
Other NICU Follow-Up Services
In addition to assessing children’s neurodevelopmental skills, experts in our clinic can also provide:
- Care coordination with pediatricians and subspecialists
- Detailed growth and nutritional recommendations
- Equipment management such as monitors and oxygen
- Help with appointments
- General Movement Assessment (GMA)
- Babies have usual, noticeable and spontaneous “general movements” from before they are born until they are 20 weeks post term. If the “general movements” are not present or they are abnormal, the infant is at higher risk of neurological problems, in particular cerebral palsy. This assessment may give information on how your baby’s neurological system is developing if there were medical concerns at birth such as prematurity, critical illness, or stroke.
- Specially trained Therapy staff at Cleveland Clinic Children’s may perform this assessment.
Referrals for:
- Early Intervention
- Occupational, Physical and Speech Therapy
- Orthotics
- Developmental Pediatrics
- Aquatic Therapy
- Power Mobility
- Augmentative Communication
- Feeding Team and Nutrition Services
- Subspecialists such as Neurology, Pulmonology, Cardiology, etc….
- Community service agencies and Social Services
- Financial assistance
We will coordinate your child’s care with you, your family pediatrician and with our specialists.
Fees
Most insurance providers reimburse visits to the NICU Follow-Up Clinic. Please check with your provider regarding coverage before your visit. Your health maintenance organization or insurance company may require pre-authorization. The referral must state the name of the physician your baby will be seeing.
Appointments
To schedule an appointment with the NICU Follow-Up clinic, please call 216.401.7575.
Locations
Cleveland Clinic Main Campus
9500 Euclid Ave.
Cleveland, OH 44195
Hillcrest Hospital
Medical Office Building II, 2nd Floor (across the street from Hillcrest Hospital)
6801 Mayfield Rd.
Mayfield Heights, OH 44124
Rocky River Medical Outpatient Center
19800 Detroit Rd.
Rocky River, OH 44116
Stow-Falls Express and Outpatient Care
857 Graham Rd.
Cuyahoga Falls, OH 44221

