Living longer is more than just growing older — it’s also about living life to its fullest
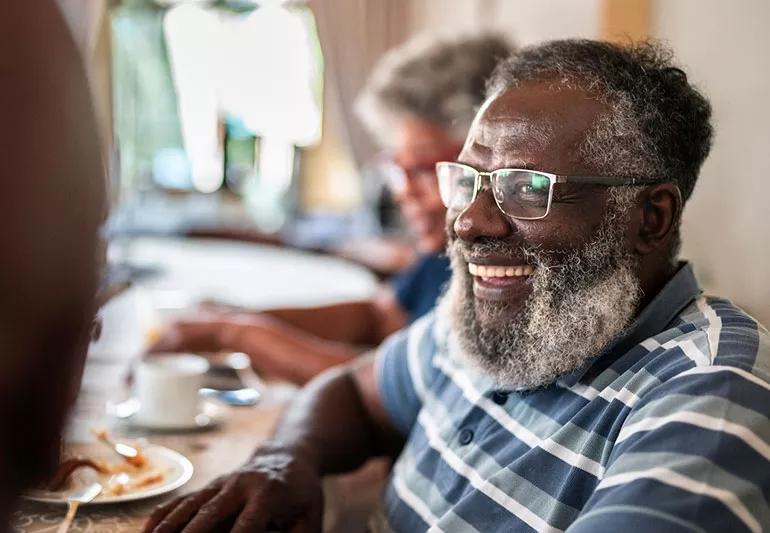

Life expectancy is increasing for people in the United States. The U.S. Census Bureau says that in 1920, 1 in 20 people in the country were age 65 or older. In 2020, that number was 1 in 6.
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Living longer should mean more time to spend with your loved ones, doing things you enjoy, making memories and cementing your legacy. Not just more time juggling the chronic and progressive ailments of older age.
“One of the greatest challenges facing older adults is preventing physical disability and extending what we call ‘active life expectancy,’” says geriatric specialist Ami Hall, DO.
That is to say spending older age living life to its fullest. They call that successful aging. It’s the difference between getting older (which we all do) and getting frailer (which we don’t necessarily all do).
Your genetics play a big role in how well you age. But your genes aren’t your destiny. Fortunately, there are steps you can take throughout your life that can help you maintain your physical, mental and cognitive health as you age. And it’s never too late to start.
Illnesses like diabetes, congestive heart failure, and some forms of dementia can be delayed or even prevented. Even loss of muscle strength with aging is at least partly preventable. And maintaining a positive outlook can help you stay mentally strong as you face illness and personal losses.
Dr. Hall shared with us advice for successful aging that can help you retain your mobility, independence and overall well-being longer.
Your physical health is one of the most important factors of successful aging. A healthy body will allow you more opportunities to do the things you enjoy.
“A lot of people look forward to things like traveling, volunteering or caring for their grandchildren after they retire. Those goals are going to be easier to meet and more enjoyable if your body is physically up to the task,” Dr. Hall notes. “The longer you can keep your body healthy and strong, the longer you can expect to live life on your own terms.”
Dr. Hall recommends these top tips for keeping healthy as you age:
An important part of successful aging is keeping your brain active. In fact, the National Institute on Aging explains that keeping your brain engaged in stimulating activities may help compensate for some of the changes that lead to things like dementia and memory loss.
“I like to recommend that people try new hobbies and practice learning new skills throughout their lives,” Dr. Hall says. “In some ways, our brains are much like our muscles — the more you work it, the better your chances of keeping it strong.”
In other words, that whole “can’t-teach-old-dogs-new-tricks” thing? Forget it. Exercising your brain can help prevent cognitive decline and ward off conditions like Alzheimer’s disease.
Try these methods to boost your brain health:
Working toward a goal requires some planning. And a goal to aging successfully is no different.
What do you want your life to look like in your 60s, 70s and beyond? What do you want to achieve? How do you want to be remembered?
Those are big questions. Some of the biggest ones. And you don’t need to have all the exact answers.
But knowing what you want from your life can inform how you care for yourself and how you plan for the future you want.
“Maintaining dignity in older age is important to a lot of people,” Dr. Hall explains. “Consider what you want your future to look like and work backward from there. Share your wishes with others. That way you can live with peace of mind knowing that your desires are understood.”
For example, if your goal is to age at home, as opposed to an assisted living facility, consider what modifications you’ll need to make it safe. Can you move to a first-floor bedroom if you have mobility concerns in the future? Who will help maintain your yard and your home if you’re unable to?
No one knows what their future holds. But preparing for the future you want is important to successful aging. You can start now with steps like:
Some people don’t like to think about getting older. Others look forward to their older years with gusto — as an opportunity to finally have the future they’ve worked their whole lives for. Either way, people are living longer than ever before.
And by caring for your health now, you can help make sure your older years are more active. More independent. And, frankly, more fun.
Learn more about our editorial process.

Chair exercises can help people age 65+ retain independence

With repeat injections over time, you may be able to slow the development of new wrinkles
The cosmetic injection may help train your muscles out of frowning, but there’s no hard data to say for sure

Turns out your health really is in your hands

When free radicals don’t have antioxidants to keep them in check, they go rogue

A look at bone buildup and loss throughout your life

Some changes in your period can be worrisome, and some not

What to look for and how to handle signs of impaired driving

Your metabolism may torch 1,300 to 2,000 calories daily with no activity

A gentle touch in all the right places may help drain your sinuses