Top Moments
1990s
Integration & Specialization
During a time of consolidation in healthcare, Cleveland Clinic built a network of regional hospitals and family health centers, integrating with Meridia Health System, Marymount, Lakewood, Fairview and Lutheran Hospitals. Within the span of three years, Cleveland Clinic transitioned from one hospital into a vast health system.
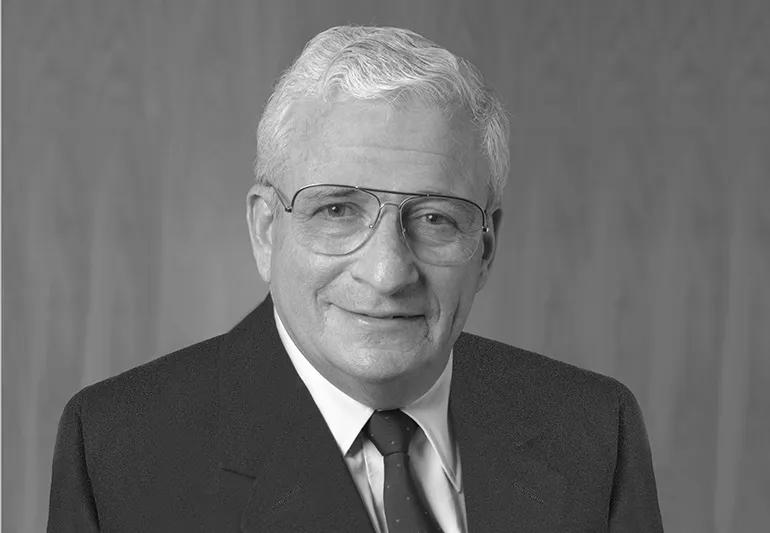

Arthur B Modell succeeds E Mandell DeWindt as President of Cleveland Clinic Foundation in 1991.
In 1991, Delos Cosgrove, MD, develops valvuloplasty techniques to repair heart valves. The Cosgrove-Edwards Annuloplasty System was a vast improvement from its predecessor and is still in use today.
In 1993 Cleveland Clinic becomes the first major medical center to publish treatment outcomes for thoracic and cardiovascular surgery, demonstrating a commitment to quality, transparency and accountability.

In 1993, Cleveland Clinic partners with Fairview and Lutheran to form the Cleveland Health Network, laying the ground for future partnerships.

Expansion in Northeast Ohio
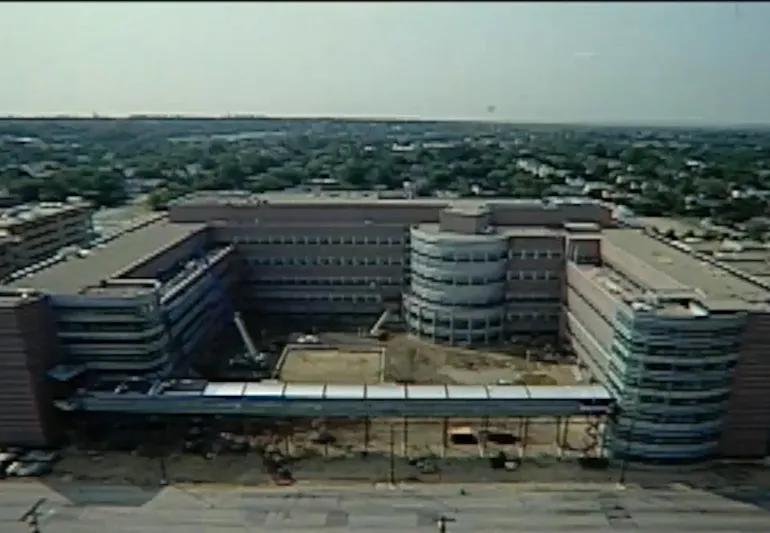
In 1993, Cleveland Clinic opens Independence Family Health Center. Family health centers opened in Westlake and Willoughby Hills in 1995 and Solon in 1996. By 2013, there were a total of 16 full-service family health centers in surrounding communities. This is the beginning of the integrated regional healthcare delivery system.
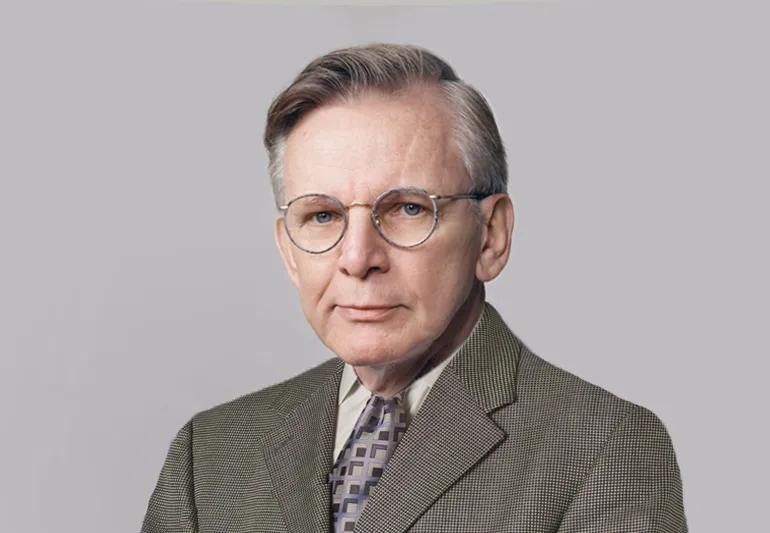

Ralph E Schey succeeds E Bradley Jones as Chair of the Board of Trustees from 1993.
In 1994, Suburban Hospital and Brentwood Osteopathic Hospital merge into South Pointe Hospital.

The first purpose-built emergency room opened on Cleveland Clinic's main campus in May 1994.
Marymount Hospital joins the Cleveland Clinic system in 1995. It was Cleveland Clinic's first regional hospital.

Alfred Lerner succeeds Arthur B Modell as President of Cleveland Clinic Foundation in 1996.

Fairview Health System – including Fairview Hospital and Lutheran Hospital – joins Cleveland Clinic in 1996.
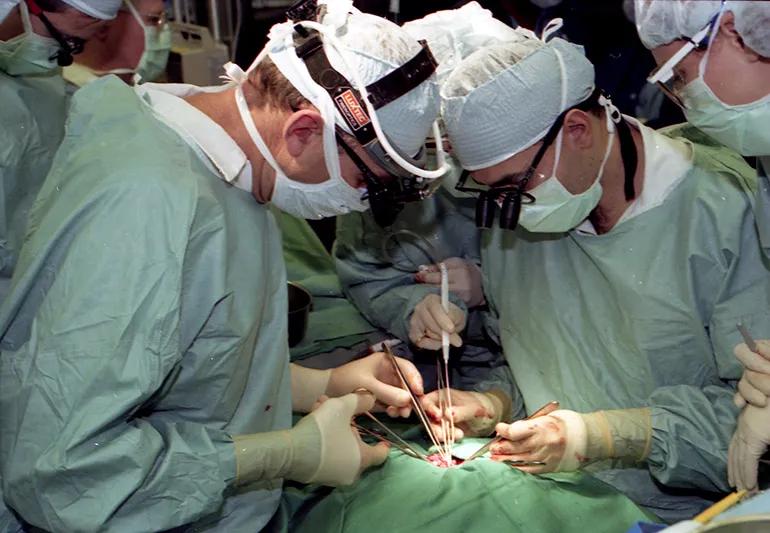
Minimally invasive heart valve surgery
In 1996, Toby Cosgrove, MD, performs the first minimally invasive heart valve surgery.
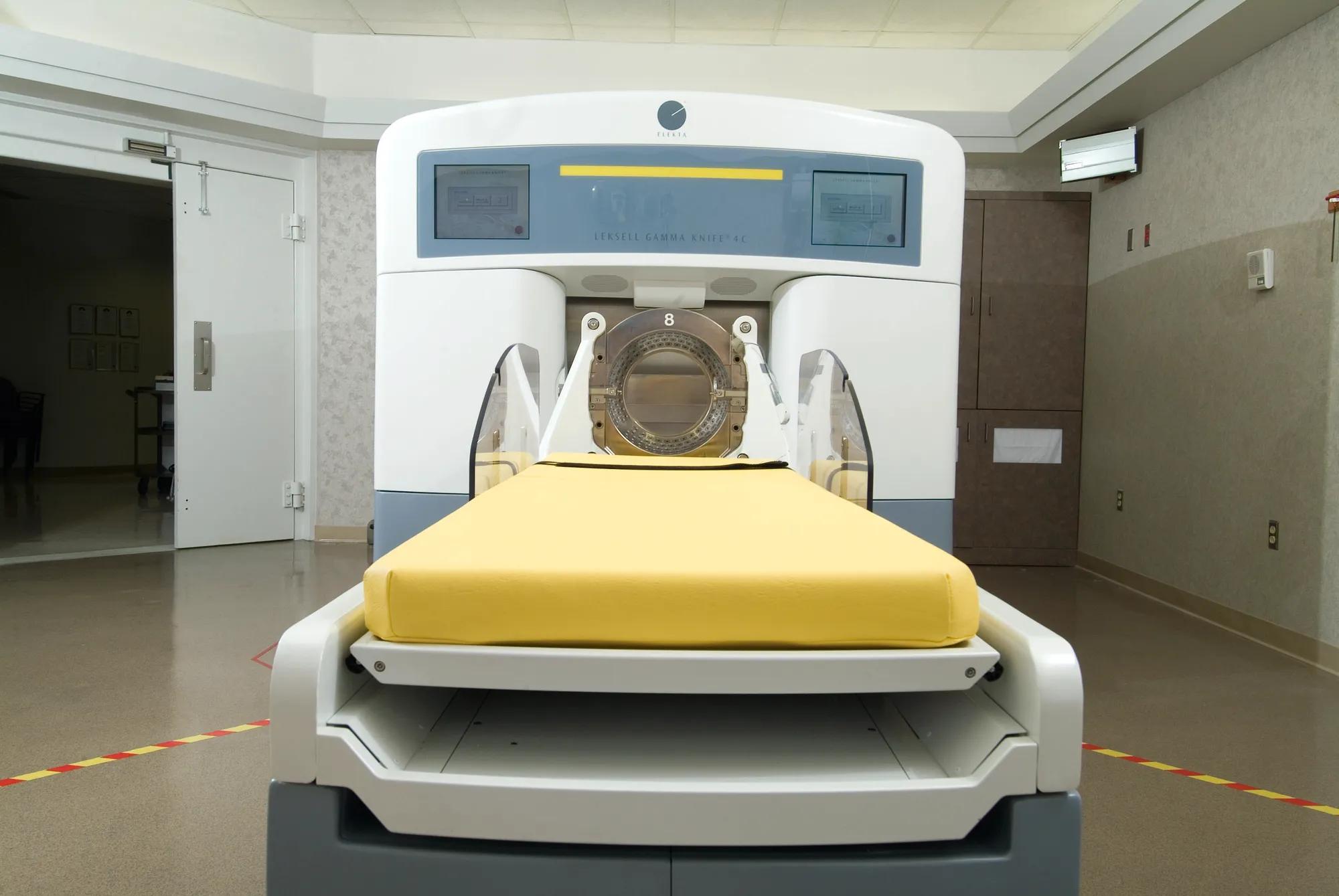

In 1997, Ohio's first Gamma Knife center opens at Cleveland Clinic.

Growth in the region
The Meridia Health System – including Hillcrest Hospital, Euclid Hospital, Huron Hospital and South Pointe Hospital – becomes part of Cleveland Clinic in 1997.

A Malachi Mixon, III succeeds Ralph E Schey as Chair of the Board of Trustees in 1997.
First successful larynx transplant
Marshall Strome, MD, former chair of otolaryngology, performed the world's first successful larynx transplant at Cleveland Clinic in 1998. To prepare himself for the operation, Dr. Strome learned and exhaustively practiced microsurgical techniques.

Pediatric urologist Robert Kay, MD, succeeds Ralph A Straffon, MD, and serves as Chief of Staff from 1999-2005.
In October 1999, construction begins on an integrated campus for Cleveland Clinic Florida. Cleveland Clinic Florida moved from Cypress Creek to Weston when this building was finished in 2001.
Main campus expansion
In the 5 years between 1999-2004, Cleveland Clinic opens the Lerner Research Institute building, the Cole Eye Institute, the Taussig Cancer Center and the Center for Genomics Research on its main campus.
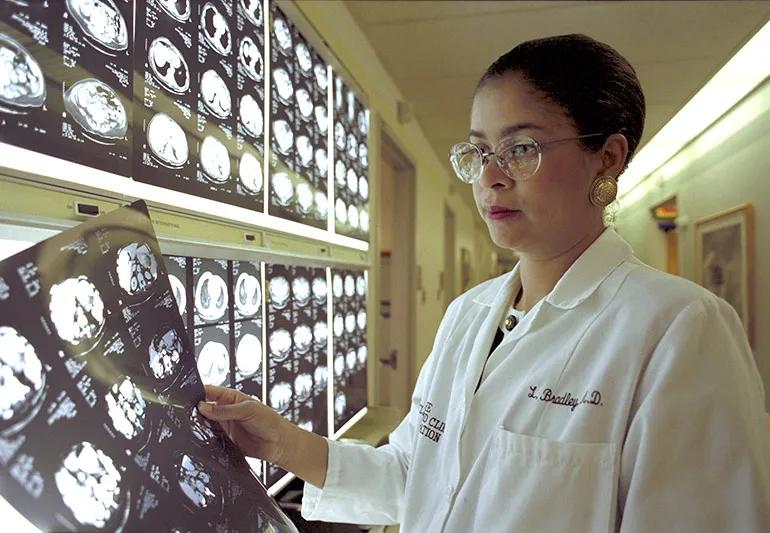
Linda Bradley, MD, views images in the late 1990s. Dr. Bradley is a gynecologic surgeon with expertise in hysteroscopy, endometrial ablation, alternatives to hysterectomy, hysteroscopic sterilization and the evaluation of abnormal uterine bleeding. She is Director of Center for Menstrual Disorders, Fibroids & Hysteroscopic Services. She was the first Black woman elected to the Board of Governors and has been named a Cleveland Clinic Bruce Hubbard Stewart Fellow, which honors physicians for compassion and clinical expertise.
