What are Uterine Fibroids?
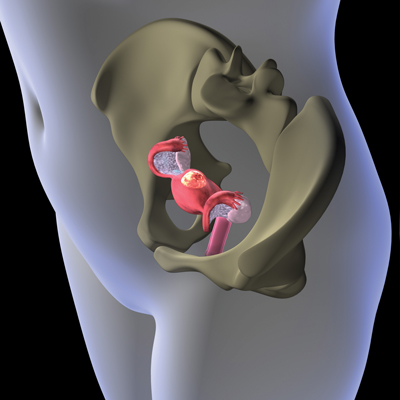
Fibroids are benign growths formed of muscle and tissue from the uterine wall. The cause of fibroids is unknown. They can be as small as a pea to as large as a watermelon. They rarely are cancerous and they don’t lead to cancer. Most fibroids occur in women of reproductive age, and according to some estimates, they are diagnosed in black women two to three times more frequently than in white women. They seldom are seen in young women who have not begun to menstruate, and the symptoms of uterine fibroids usually stabilize or go away in women after menopause.
Risk Factors
Are there any known risk factors for uterine fibroids?
Risk factors for uterine fibroids include obesity, family history, not having children, early onset of menstruation and late age for menopause. (A woman is considered obese if she is more than 20 percent over her ideal body weight.)
Symptoms

What are the symptoms of uterine fibroids?
In most cases, fibroids do not cause any symptoms and do not require treatment other than regular observation by a doctor. But some women who have uterine fibroids may experience the following symptoms:
- Excessive or painful bleeding during menstruation
- Bleeding between periods
- A feeling of fullness in the lower abdomen
- Frequent urination resulting from a fibroid that compresses the bladder
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Low back pain
- Constipation
- Chronic vaginal discharge
- Inability to urinate
- Urinary urgency
- Severe menstrual cramps
- Infertility
What else can cause problem bleeding?
Heavy bleeding is a symptom of many things that can go wrong with not just the uterus, but with the body in general. The most common structural causes are fibroids and polyps, which account for heavy bleeding in about 40 percent of women. The remaining causes are often hormonal, related to aging or changes in the endocrine system. Obesity is another hormonally-based cause of heavy bleeding.
Sexually transmitted diseases such as gonorrhea and chlamydia can cause bleeding between periods and produce painful menstruation. Heavy bleeding may sometimes be associated with a gynecologic cancer. This is why a comprehensive evaluation must be undertaken. While the chances of a gynecologic malignancy are low, your healthcare provider will determine the appropriate clinical testing to exclude cancer.
Anemia Clinic
Women with menstrual disorders are particularly susceptible to anemia, which can cause symptoms including fatigue, depression, shortness of breath, hypotension and heart palpitations. In nonpregnant women, anemia is defined as a hemoglobin level less than 12 g/dl, or a hemotocrit less than 36 percent. In the Center for Menstrual Disorders, Fibroids and Hysteroscopic Services, patients are evaluated for anemia with simple laboratory testing. When anemia is diagnosed, women are referred to the anemia/blood conservation program for treatment, which usually begins with iron supplementation. Patients are followed until blood levels are normal.
Fibroids Evaluation
How are fibroids evaluated?
An extensive workup can pinpoint the cause, location and/or extent of fibroids or menstrual difficulties. We begin with a detailed menstrual and health history, and a gynecologic exam. Then we use one of the following imaging techniques to determine the health of your uterus before proceeding with treatment:
Office hysteroscopy: use of a lighted tube, or endoscope, inserted through the vagina to examine the uterus. (Cleveland Clinic specialists have cumulatively performed more than 10,000 office hysteroscopies.)
Saline infusion sonography: a type of transvaginal ultrasound performed in the office that utilizes a small catheter placed through the cervix into the uterus. It is used to infuse a few tablespoons of salt water (saline) to provide excellent imaging of the uterine anatomy. This test can evaluate for ovarian masses, uterine polyps, uterine fibroids, pre-cancerous and cancerous conditions.
MRI: combining a powerful magnet, radio signals and a computer to obtain intricate pictures of the uterus and surrounding organs. This test is more commonly utilized when your physician is considering your candidacy for uterine fibroid embolization, extensive myomectomy, or to determine whether you are a candidate for a laparoscopic procedure.
We also ask every woman we see whether or not she wants to preserve her fertility and/or her uterus. These considerations are very important in determining which treatments we will recommend. We aim for the best treatment outcome and the highest patient satisfaction.
Treatments

How are fibroids treated?
Following your evaluation, we will openly discuss all treatment options available to you. Treatments may involve medical management, nonsurgical solutions, or minimally invasive or standard surgery. Sometimes your age and proximity to menopause may determine the type of therapy offered. Women who desire fertility may not be offered certain surgical procedures.
Nonsurgical therapy
Current medications typically treat only the symptoms of fibroids. For women who experience occasional pelvic pain or discomfort, a mild, over-the-counter anti-inflammatory or pain-killing drug such as Naproxen™ or ibuprofen often will be effective. More bothersome cases may require stronger drugs available by prescription. Additionally, these medications may decrease the amount of menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, clotting and gushing of blood that some women experience.
Some fibroids are treated with hormones that reduce the amounts of the hormone estrogen. Birth control pills (oral contraceptives) can be used to treat the bleeding symptoms and menstrual cramps caused by uterine fibroids because they decrease the production of female hormones and prevent ovulation. Birth control pills do not reduce the size of uterine fibroids, but often help to alleviate symptoms related to fibroids and regulate menses, and decrease the quantity of bleeding and cramps. Oral contraceptives rarely contribute to the growth of fibroids.
Another medical treatment for menstrual disorders is Mirena®. This progesterone intrauterine system can be placed into the uterus during an office visit. Mirena is a method of contraception, but has the added benefit of dramatically decreasing the amount of bleeding, cramps and menstrual flow. In fact, up to 50 percent of patients experience temporary cessation of menstrual cycles. If desired, the Mirena system can safely remain in place for up to five years.
If periods are irregular due to obesity, a nutrition consultation is advised. After a thorough clinical evaluation, you may be referred to a bariatric specialist on our team who may advise bariatric surgery to help you manage your weight and improve your nutrition.
Finally, we offer alternative treatments for problems such as severe cramping, to promote healing and relaxation, and to reduce stress. Alternative techniques include acupuncture, massage, Reiki, and yoga for stress reduction and healing. We offer group sessions for women in conjunction with our Wellness Institute.
Surgical Options: For Women Who Want to Preserve Fertility
We believe that when surgery is indicated, a patient benefits from the care of a high-volume gynecologic surgeon. Our gynecologists are national and internationally recognized surgeons for their broad surgical experience. It has been demonstrated that women needing surgery, benefits from gynecologic surgeons who maintain a busy surgical practice. This translates into fewer complications, less surgical time, decreased overall costs, and excellent clinical outcomes. If surgical intervention is warranted, our specialists are experts in many less invasive options for the treatment of uterine fibroids that can control symptoms, preserve the uterus and preserve fertility. We routinely treat complex cases and are experienced in performing surgery on women with multiple co-morbidities and significant medical problems, and overweight, obese women, for whom surgery is risky.
If a fibroid is particularly symptomatic, the surgeon often can remove only the fibroid, leaving the uterus intact. This procedure is called myomectomy. This is done when a woman wants to be able to have children or wishes to retain her uterus as a personal choice.
There are a number of techniques that can be used to perform a myomectomy. The appropriate procedure is determined by the size, number and location of the fibroids, and physician’s surgical expertise.
Laparoscopic and single-port myomectomy, or robotic myomectomy involves the use of a thin, telescope-like instrument attached to a small video camera called a laparoscope inserted through a tiny incision at the belly button. The surgeon uses specialized surgical instruments inserted through this incision with one or more thumbnail-sized additional small incisions in the abdomen to remove the fibroids. Patients are often able to be discharged home within a few hours or only require a 23-hour stay in the hospital.
Hysteroscopic myomectomy is a procedure in which some fibroids are removed through the vagina using a surgical instrument called a hysteroscope (a thin, telescope-like instrument inserted through the cervix and into the uterus). This does not require any abdominal incisions. Hysteroscopic myomectomy most often is a same-day surgery, which permits patients to return to work within two days. This technique can be employed when fibroids are within the uterine cavity.
Laparotomy involves an abdominal incision to remove all fibroids and is most often employed when excessive size and number of fibroids are present. Our surgeons, when possible, utilize cosmetically placed incisions and minimally invasive techniques to facilitate quick recovery.
Surgical Options: For Women Not Interested in Having Children
There are two additional surgical options to end excessive bleeding without removing the uterus in reproductive-aged women who have completed childbearing.
Endometrial ablation
Some women, despite having very small uterine fibroids or a normal uterus, experience excessively heavy menstrual cycles. For women who fail medical therapy and do not desire children, endometrial ablation most commonly decreases the amount and duration of menses. Endometrial ablation can be performed in the office, generally taking less than 10 minutes. A thin layer of the uterine lining is destroyed, leading to a marked decline in the amount of menstrual bleeding.
Uterine fibroid embolization (UFE)
Cleveland Clinic gynecologists collaborate with Cleveland Clinic interventional radiologists to perform uterine fibroid embolization for women who have symptomatic fibroids and do not plan on having children. This procedure generally takes less than 60 to 90 minutes to perform, with minimal sedation. A slender catheter is placed under X-ray guidance into the uterine artery, and tiny particles are then injected to block the flow of blood to the fibroid. Robbed of oxygen and nutrients, the fibroid shrinks over a period of months.
Hysterectomy
Fibroids can grow back. For some women, especially those who are ready to enter menopause, hysterectomy (surgically removing the uterus) is a reasonable alternative. Cleveland Clinic gynecologic surgeons are experts in minimally invasive forms of hysterectomy and are pioneers in robotic and single-port hysterectomy. With many modalities available to perform hysterectomy, our physicians will determine which route is best based on the size, number and location of your fibroids, and other clinical indicators.
Abdominal hysterectomy
“Open” abdominal hysterectomy is one of the most common surgeries performed in the United States. It involves removing the uterus through an incision at the bikini line. Cleveland Clinic specialists prefer to use less invasive alternatives whenever possible.
Vaginal hysterectomy
In this approach, the uterus is removed through an incision in the vagina, which avoids an abdominal incision and scar.
Laparoscopic hysterectomy
Some patients are eligible for removal of the uterus through slender instruments inserted into the abdomen using a laparoscope. In laparoscopic surgery, several tiny incisions are made in the abdomen so that a miniature camera and special instruments can be inserted. Benefits include a 23-hour hospital stay, less need for postoperative pain medications and faster return to activity.
Robotic hysterectomy
This advanced form of laparoscopy involves the use of robotic instruments guided by tiny 3-D cameras. The surgeon controls robotic arms that carefully remove the uterus and precisely suture tissue. Only small abdominal incisions are required. Similar outcomes to laparoscopic hysterectomy are also noted including decreased postoperative pain, decreased need for pain medications and quicker return to normal activities.
Single-port hysterectomy
This procedure utilizes one incision in the belly button. It has similar outcomes when compared to laparoscopic and robotic approaches. An additional benefit is that there is only one belly button incision.
Patient Services
MyChart
Cleveland Clinic's MyChart is a secure, online tool that connects you to portions of your electronic medical record from the privacy of your home. Utilize this free service to manage your healthcare at any time, day or night. With MyChart you can view test results, renew prescriptions, request appointments and more. You can also manage the healthcare of your loved ones with MyChart • Caregiver.
Appointments & Locations
Contacting Cleveland Clinic
Ready to Schedule an Appointment with a Specialist?
If you would like to set up a consultation with a Cleveland Clinic specialist in the Center for Menstrual Disorders, Fibroids and Hysteroscopic Services, please call 216.444.6601 or 800.223.2273, ext. 46601. If you are seeking a second opinion, please remember to bring your outside records, X-ray, and laboratory results with you so than we can provide the most comprehensive evaluation and minimize duplicate testing.
Still Have Questions?
We welcome your questions and concerns. For additional information, call our specially trained Women’s Health Nurse Advocate at 216.444.4HER (4437).
Virtual Second Opinion
If you cannot travel to Cleveland Clinic, help is available. You can connect with Cleveland Clinic specialists from any location in the world via a phone, tablet, or computer, eliminating the burden of travel time and other obstacles. If you’re facing a significant medical condition or treatment such as surgery, this program provides virtual access to a Cleveland Clinic physician who will review the diagnosis and treatment plan. Following a comprehensive evaluation of medical records and labs, you’ll receive an educational second opinion from an expert in their medical condition covering diagnosis, treatment options or alternatives as well as recommendations regarding future therapeutic considerations. You’ll also have the unique opportunity to speak with the physician expert directly to address questions or concerns.
Locations
Why Choose Us?
In our center, we put patients first. We individualize the evaluation and treatment of each woman we see, taking into account her preferences about preserving her fertility, and her desire for minimally invasive surgical procedures or medical therapy. This patient-centered philosophy reaffirms our commitment to offer alternatives to hysterectomy, including the latest hysteroscopic, standard or single port laparoscopic, robotic, or radiologic techniques; or medical therapy.
Menstrual disorders are the number one reason that women seek help from a gynecologist Uterine fibroids occur in 50 to 80 percent of women. Half of these women have no symptoms. However, the other half may experience a constellation of symptoms ranging from heavy or irregular menstrual cycles to pelvic cramping, back pain, urinary frequency, infertility or abdominal swelling. Fibroids may be discovered during routine gynecologic examinations, pelvic imaging or during prenatal care. When fibroids are asymptomatic, they do not require treatment other than regular observation by a doctor.
When uterine fibroids cause symptoms, Cleveland Clinic experts can help. The Center for Menstrual Disorders, Fibroids and Hysteroscopic Services in the Ob/Gyn & Women’s Health Institute uses a unified, streamlined, interdisciplinary approach to evaluate your problem and arrive at the best treatment solution for you.